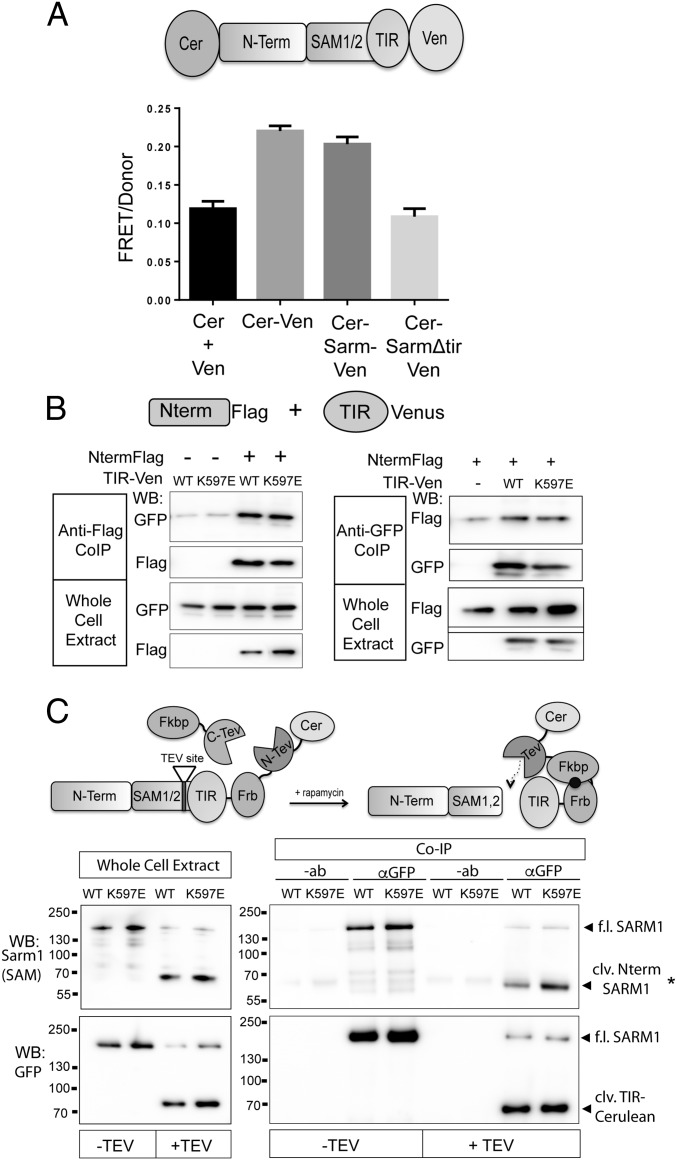
Fig. 7.
SARM1 N terminus and TIR domain form a physical complex. (A) FRET pairs Cerulean and Venus were attached to the N terminus and C terminus of SARM1, respectively (CerSARMVen). The FRET/donor ratio in DRGs from CerSARMVen was higher than Cerulean and Venus expressed in trans (Cer + Ven) and comparable to a direct Cerulean-Venus fusion. Deletion of the SARM1 TIR domain reduces FRET signal to background levels. (B) N terminus (Nterm) of SARM1 tagged with a Flag epitope was expressed in HEK293T cells with the TIR domain (WT or K597E) tagged with Venus. Error bars reflect ± SEM (n = 3). TIR-Venus was immunoprecipitated from HEK293T cell extracts, and the coimmunoprecipitated Nterm was assessed by Western immunoblotting (WB) for Flag. Nterm Flag was immunoprecipitated from cell extracts, and coimmunoprecipitated TIR-Venus was assessed by Western immunoblotting for GFP. Western blots are reflective of four independent experiments. (C) SARM1ps was transfected in HEK293T cells with or without Fkbp-C-TEV to cleave an engineered TEV site upstream of the TIR domain. (Left) WB of whole-cell extracts shows efficient proteolysis to generate cleaved (clv.) Nterm SARM1 containing Nterm and SAM domains, detected with antibody that recognizes peptide in the SAM2 domain of SARM1. Proteolysis also generates a fragment containing the SARM1 TIR domain tagged with Cerulean (detected with GFP antibody). TIR-Cerulean was immunoprecipitated with GFP antisera or antibody (−ab) as a control. In the presence of Fkbp-C-TEV (+TEV), a bound SARM1 fragment containing Nterm/SAM domains is detected with anti-SARM1 antibody by Western blot (*clv. Nterm SARM1). (Lower) GFP WB detecting immunoprecipitated TIR-Cerulean. Western blots are representative of five independent experiments. Co-IP, coimmunoprecipitation; f.l., full length.