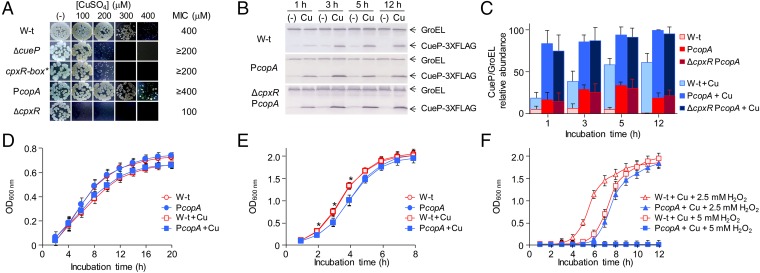
Fig. 2.
Coordinated regulation of cueP is required for optimal growth. (A) Comparative Cu MIC values in wild-type (W-t) Salmonella, ΔcueP, cpxR-box*, PcopA, and ΔcpxR mutant strains on LB plates containing increasing amounts of CuSO4 in anaerobic conditions. (B) Detection of CueP in whole-cell extracts obtained from the cueP-3×FLAG (WT), the PcopA-cueP-3×FLAG mutant strain (PcopA), and the PcopA-cueP-3×FLAG in the ΔcpxR mutant strain (ΔcpxR PcopA), grown in LB without or with the addition of 1 mM CuSO4. Here, 20 µg of total protein cell extracts was analyzed by SDS/PAGE, followed by transfer to nitrocellulose and development using monoclonal anti-FLAG antibodies. CueP relative levels were normalized to GroEL. (C) Mean value of three biological replicates analyzed in duplicate in each case. (D and E) Wild-type Salmonella and the PcopA-cueP mutant strain growth in static/microaerobic (D) or in aerobic conditions (E) in LB without or with the addition of sublethal concentrations of CuSO4. The data correspond to mean values of at least four independent experiments performed in duplicate. *Significant differences in growth (P < 0.005) from the wild-type to the PcopA mutant strains grown aerobically in either the absence or the presence of Cu. (F) Wild-type Salmonella and the PcopA-cueP mutant strain growth in LB with sublethal concentrations of CuSO4 and with the addition of 2.5 or 5 mM H2O2. The data correspond to mean values of at least four independent experiments performed in duplicate.