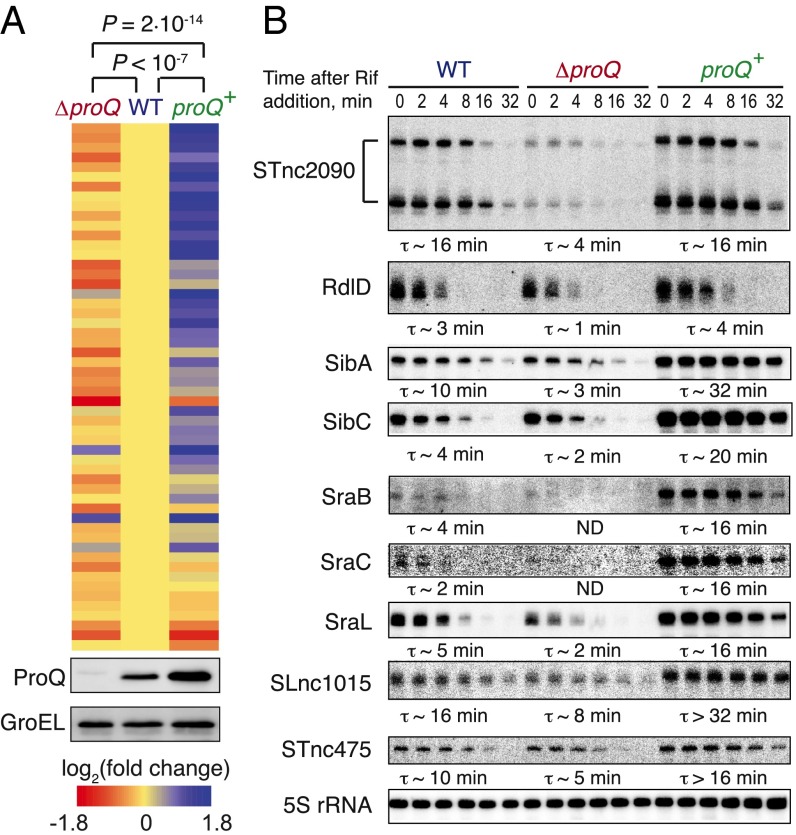
Fig. 5.
ProQ acts as a stability factor for most of its sRNA ligands. (A) ProQ positively affects the steady-state levels of most of its sRNA ligands. The heat map shows the changes in the abundance of ProQ-associated noncoding RNAs (n = 54) upon proQ deletion (ΔproQ) or complementation (proQ+). Significance of the differences is evaluated by Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-ranks test. (Lower) Corresponding levels of ProQ in these strains, as revealed by Western blotting with a ProQ-specific antiserum. Only those sRNAs that have been sufficiently covered in the transcriptome dataset are shown. (B) ProQ stabilizes its associated sRNAs in vivo. Samples from WT, ΔproQ, and complemented proQ+ strains were collected in the stationary phase after transcription arrest with rifampicin and analyzed by Northern blotting. Approximate half-lives for major detected species are shown below the blots. ND, not determined (<1 min). A representative of three independent experiments is shown.