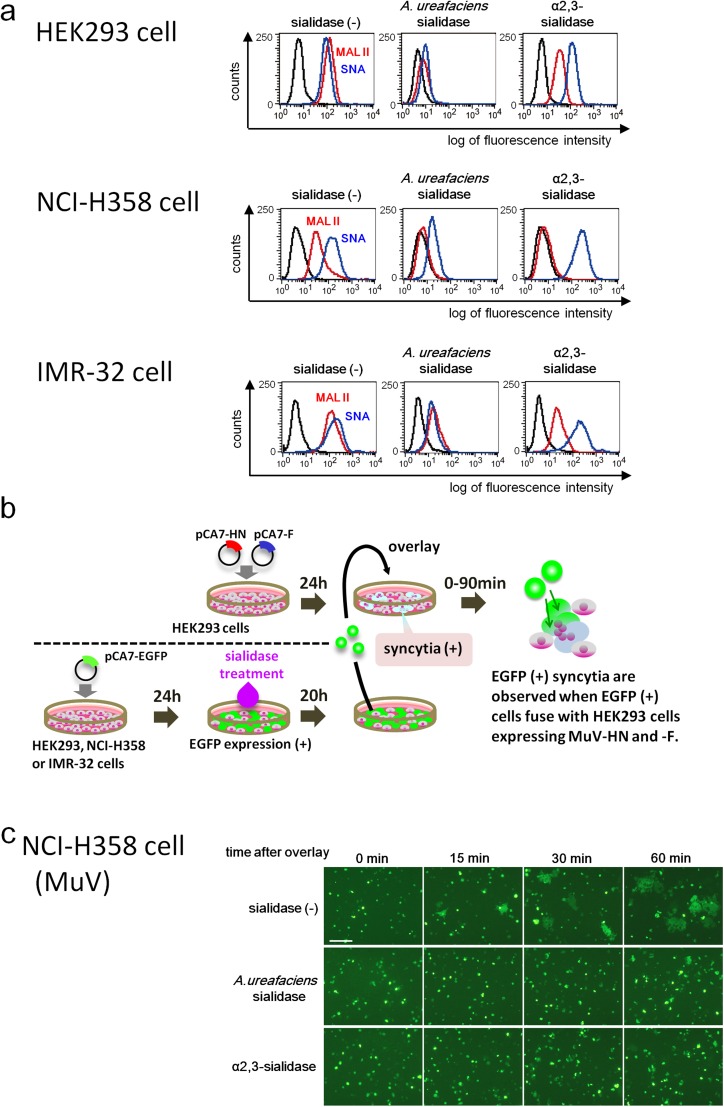
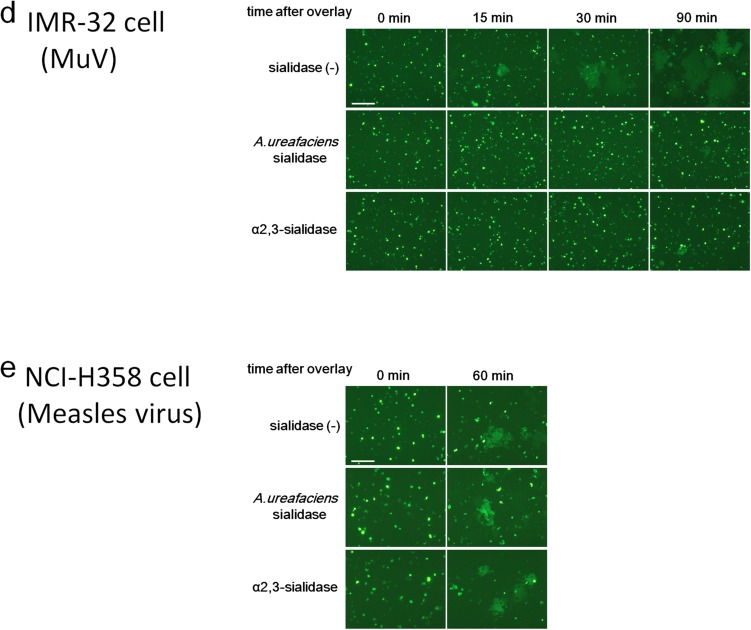
Fig. S5.
Effect of cleavage of sialic acid on MuV-induced cell–cell fusion. (A) HEK293 cells, the respiratory epithelial cell line NCI-H358, and the neuroblastoma cell line IMR-32 were treated with control medium, A. ureafaciens sialidase, or S. typhimurium α2,3-sialidase. The treated cells were incubated with biotinylated MAL II, SNA, or control medium and then with FITC-avidin. They were analyzed on a FACSCalibur cell analyzer (BD Biosciences). (B) Schematic of the experimental procedure of the cell–cell fusion assay. (C and D) NCI-H358 cells (C) and IMR-32 cells (D) expressing EGFP were treated with control medium, α2,3-sialidase, or A. ureafaciens sialidase. They were detached from the plates and then overlaid onto HEK293 cells expressing the HN and F proteins of MuV. The cells were observed using fluorescent microscopy for up to 60 or 90 min after overlay. (E) Measles virus-induced cell–cell fusion was examined as a control. Sialidase-treated NCI-H358 cells were overlaid onto HEK293 cells expressing the H and F proteins of measles virus, and observed at 0 min and 60 min after overlay. (Scale bar: 200 µm.) The data are representative of three independently performed experiments.