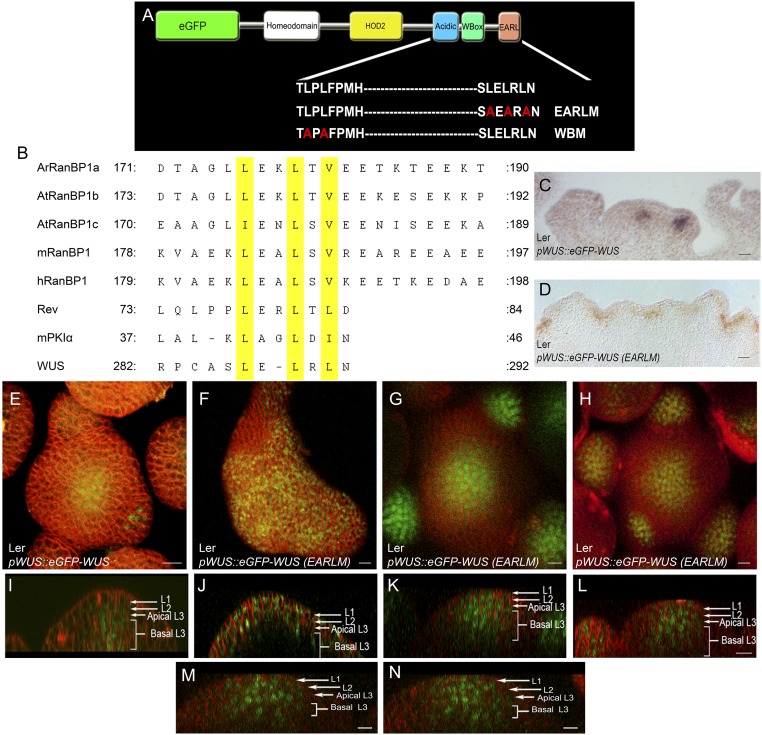
Fig. S2.
The EAR-like domain influences nuclear accumulation of WUS. (A) A schematic of WUS protein domains showing amino acid sequences of the WT, the mutant WUS-box domain, and the mutant EAR-like domain (EARLM). Amino acid substitutions are shown in red. (B) Sequence alignment of nuclear export signals (NESs) of RAN binding proteins (RanBPs) from Arabidopsis, mouse, human, HIV1 protein Rev, and heat stable inhibitor of cAPK (mPKIα) along with the EAR-like domain of WUS. The leucine residues are highlighted in yellow. RNA in situ with WUS anti-sense probe in (C) pWUS::eGFP-WUS and (D) one of the enlarged IMs of pWUS::eGFP-WUS (EARLM). E and I are the 3D top and side views of IM expressing pWUS::eGFP-WUS. (F–H) and (J–L) are the 3D top and side views of three independent IMs expressing pWUS::eGFP-WUS (EARLM). M and N are side views of different sections of an IM expressing pWUS::eGFP-WUS (EARLM). The cell layers in SAMs are indicated by white arrows and brackets. eGFP-WUS (green) and FM4-64 (red). (Scale bars: 10 μm, except F, 15 μm and D, 30 μm.)