FIG 10.
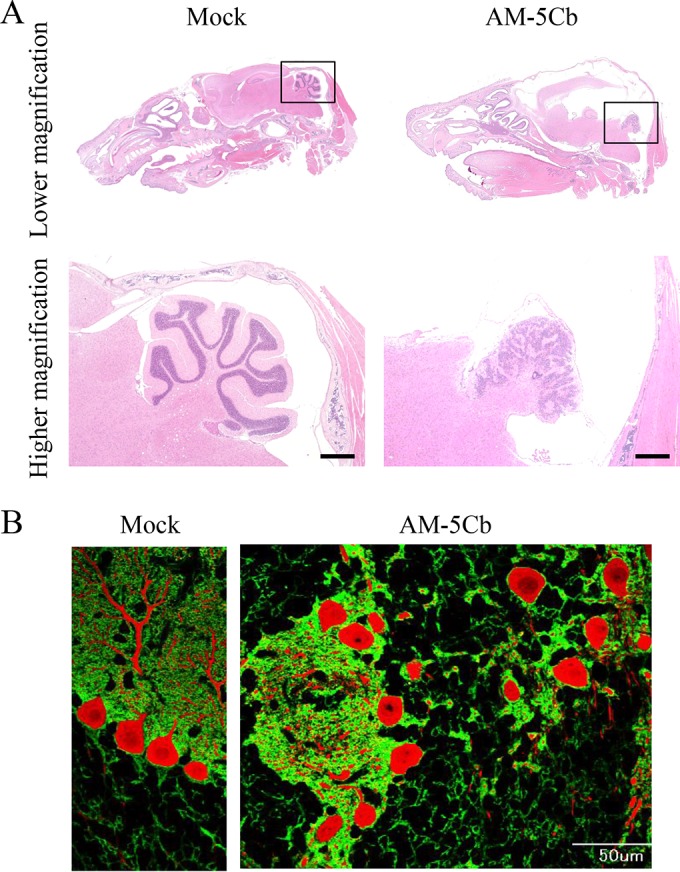
High titers of the mouse-passaged SAFV-3 strain induce malformation of the cerebellar cortex in neonatal ddY mice. Within 24 h of birth, neonatal ddY mice were intracerebrally inoculated with the mouse-passaged AM-5Cb strain of SAFV-3 at 106 CCID50s/10 μl. (A) H&E staining. (B) Double immunofluorescence staining with anti-GLAST (radial astrocytes; green) and anti-calbindin (Purkinje cells; red) antibodies. (Left side of panels A and B) Representative sagittal brain sections from a mock-infected neonatal mouse at day 19 postinjection with 2MEM. (Right side of panels A and B) Representative sagittal brain sections from an AM-5Cb-inoculated neonatal mouse at day 19 p.i. The arbor vitae of the cerebellum appear normal in the mock neonatal mouse (left side of panel A). In contrast, hydrocephalus of the cerebral cortex and small cerebella are evident in all four AM-5Cb-inoculated neonatal mice (upper right side of panel A). The arbor vitae of the cerebellum are unclear in the AM-5Cb-inoculated mouse (lower right side of panel A). The cerebellar cortex of the mock-inoculated mouse can be divided into three layers: the molecular layer, the Purkinje cell layer, and the granular layer (left side of panel B). In contrast, the three layers are not apparent in the cerebellar cortex of the AM-5Cb-inoculated mouse (right side of panel B). Original magnifications: top of panel A, ×20; bottom of panel A, ×100; panel B, ×400. Bars, 500 μm (bottom of panel A) and 50 μm (right side of panel B).
