FIG 4.
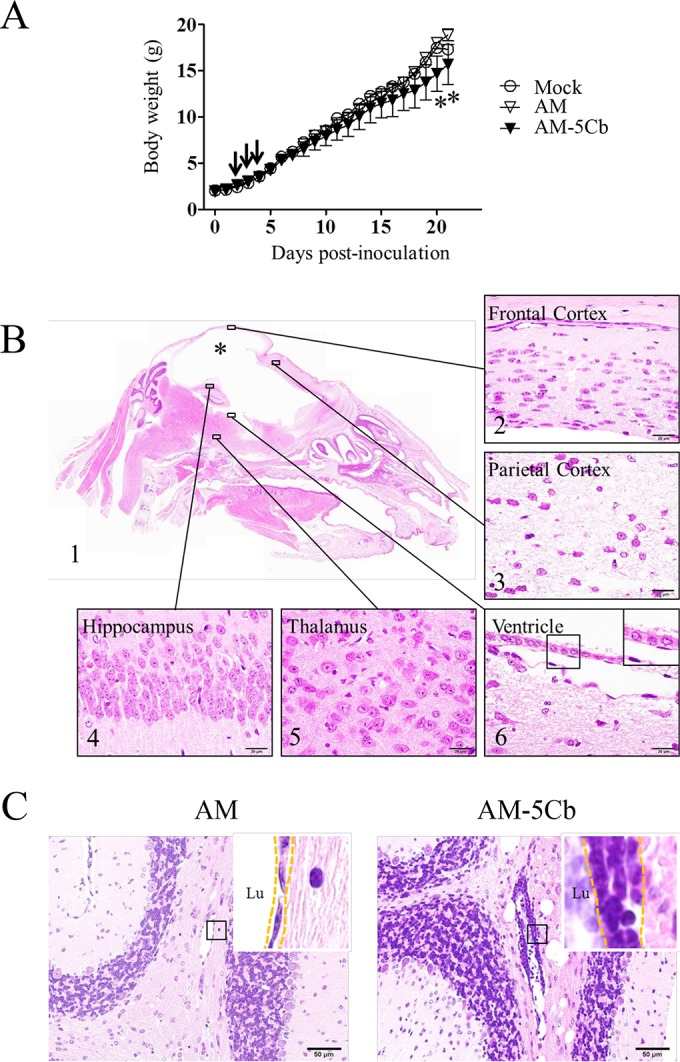
Neurovirulence of mouse-passaged SAFV-3 in neonatal ddY mice. Within 24 h of birth, neonatal ddY mice were inoculated intracerebrally at 104 CCID50s/10 μl with SAFV-3 derived from a case of aseptic meningitis (AM strain) or with mouse-passaged SAFV-3 (AM-5Cb strain). (A) Body weights of neonatal ddY mice after SAFV inoculation. Animals were observed for clinical manifestations, and body weights were measured daily for 21 days (n = 4). One AM-inoculated mouse showed mild neurological signs, including rolling and ataxia, from days 7 to 9 p.i., whereas some AM-5Cb-inoculated mice showed obvious rolling and ataxia from days 2 to 4 p.i. (arrow). On days 20 and 21 p.i., AM-5Cb-inoculated mice showed significantly less weight gain than mock-infected control mice (*, P < 0.05; one-way ANOVA). (B, C) Sagittal brain sections of representative neonatal ddY mice intracerebrally infected with the AM or AM-5Cb strain on day 21 p.i. H&E staining. The cystic lesion (asterisk) is filled with CSF, and the cerebral cortex is nearly absent (B1). The brainstem and cerebellum remain. Thinning of the cerebral cortex (B2) and severe necrosis (B3) are observed in the residual cerebral cortex. The hippocampus (B4) and thalamus (B5) appear normal. The cystic lesion in the cerebrum is lined with ciliated ependymal cells (B6, inset). Perivascular inflammation (C, dotted frame in inset) is observed in the cerebellar medulla of AM-5Cb-inoculated mice (C, right side) but not in that of AM-inoculated mice (C, left side). Lu, lumen. Original magnifications, ×20 (B1), ×400 (C), and ×1,000 (B2, -3, -4, -5, and -6 and all insets). Bars, 20 μm (B) and 50 μm (C).
