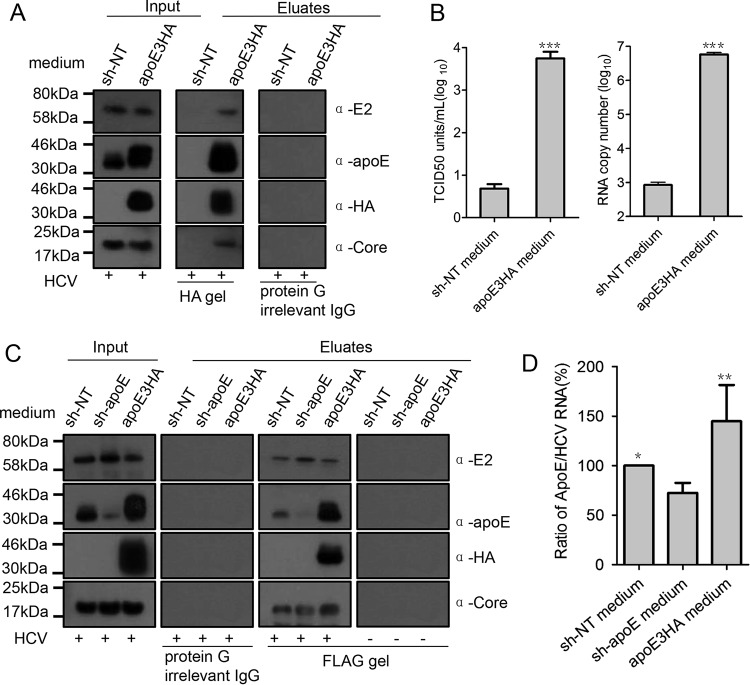
FIG 8.
apoE is exchanged to HCV LVPs for their high apoE levels. (A) Flag-tagged HCV produced from Huh7.5.1 cells was mixed with equal volumes of sh-NT medium and apoE3HA medium and incubated for 4 h at 37°C. Afterwards, HA affinity purification of HCV LVPs was conducted to evaluate mobilization of apoE3HA to HCV LVPs. After HA affinity gel purification, HCV E2, apoE3HA, and core protein in eluates were detected by Western blot analysis. (B) Infectivity and genome copy number of eluates were detected by limiting-dilution assay and quantitative reverse transcriptase PCR (qRT-PCR), respectively. Input and eluted proteins are shown. Molecular sizes are indicated on the left, and proteins are specified on the right. (C) Flag-tagged HCV produced from Huh7.5.1 cells was mixed with equal volumes of sh-NT medium, sh-apoE, and apoE3HA medium and incubated for 4 h at 37°C. Afterwards, Flag affinity purification of HCV LVPs was conducted to reevaluate mobilization of apoE3HA to HCV LVPs. After Flag affinity gel purification, HCV E2, apoE3HA, and core protein in eluates were detected by Western blot analysis. (D) ApoE abundance on Flag affinity-purified LVP was evaluated by calculating the ratio of apoE amount to genome copy number. Shown are the means from 3 independent experiments; error bars indicate standard deviations from the means.