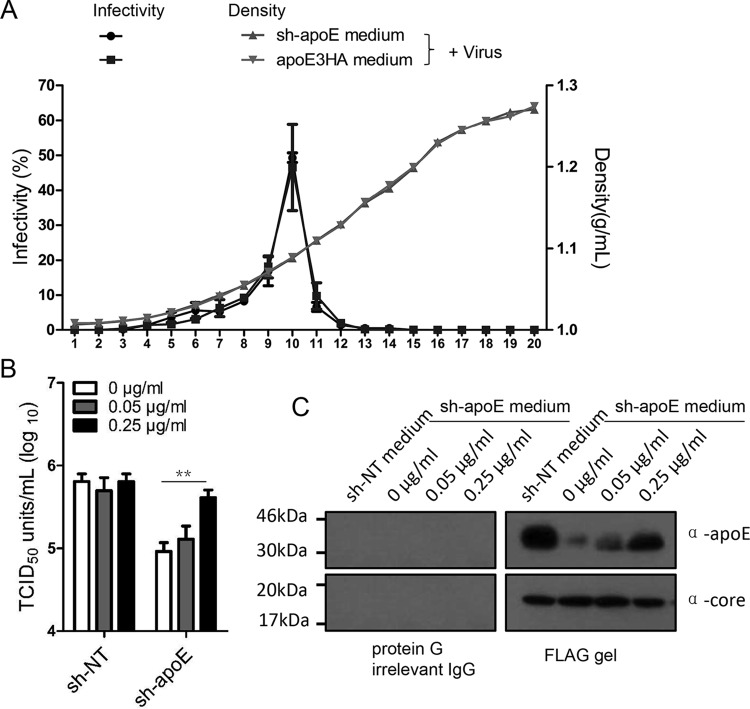
FIG 9.
Lipid-free apoE enhances HCV infection in apoE knockdown cells. (A) Biophysical property of HCV LVPs conditioned with sh-apoE medium and apoE3HA medium. One milliliter of HCV produced from Huh7.5.1 cells was mixed with 30 ml of either sh-apoE medium or apoE3HA medium. The mixture was incubated for 4 h at 37°C, followed by concentration by ultrafiltration and fractionation by density gradient centrifugation. The virus infectivity of each fraction was determined as described above. Shown are the means of 3 independent experiments; error bars indicate standard deviations from the means. (B) Different amounts of lipid-free apoE were added into 96-well plates containing either Huh7.5.1 or sh-apoE cells. The final concentrations of lipid-free apoE were 0, 0.05, and 0.25 μg/ml. Infectivity of HCV was tested in these plates afterwards. Shown are the means of 3 independent experiments; error bars indicate standard deviations from the means. (C) Flag-tagged HCV produced from Huh7.5.1 cells was mixed with equal volumes of sh-NT medium with different amounts of lipid-free apoE. The mixture was incubated for 4 h at 37°C. Flag affinity purification of HCV LVPs was conducted to evaluate the apoE amounts on HCV LVPs by Western analysis. Molecular sizes are indicated on the left, and proteins are specified on the right.