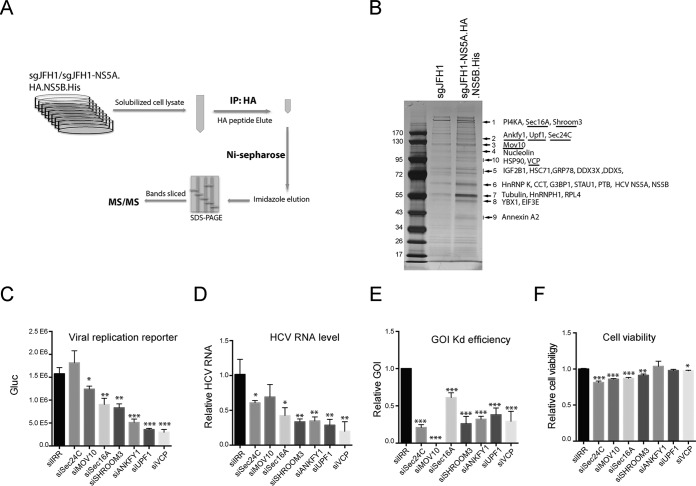
FIG 3.
Identification of host factors associated with the HCV protein complex. (A) Schematic of two-step affinity purification of the HCV protein complex and identification of associated host proteins. IP, immunoprecipitation. (B) After two-step affinity purification, the eluted proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE. Specifically, enriched protein bands (arrows) in the sgJFH1-NS5A.HA.NS5B.His sample were identified by MS. Previously reported HCV-interacting host proteins and identified viral proteins in the bands indicated are shown. Host factors selected for further study are underlined. (C to F) siRNA screening of selected host factors. Huh7.5 cells were transfected twice with siRNAs against host factors at a final concentration of 30 nM and then infected with Jc1G at an MOI of 0.1 for 2 days. The values to the left are molecular sizes in kilodaltons. (C) Gaussia luciferase (Gluc) activity in the supernatants from infected cells are shown. Mean values ± standard deviations are shown (n = 3). (D) HCV RNA levels in the infected cells were quantified by quantitative RT-PCR and normalized against GAPDH RNA levels. HCV RNA levels relative to siIRR (irrelevant target) are shown. Mean values ± standard deviations are shown (n = 3). (E) RNA levels of specific host factors were quantified and normalized against GAPDH RNA levels. RNA levels relative to siIRR are shown. Mean values ± standard deviations are shown (n = 3). (F) Before HCV infection, cell viability was measured and normalized against siIRR. Mean values ± standard deviations are shown (n = 3). Statistical analysis was performed by comparing the siGOI and siIRR groups (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001, two-tailed, unpaired t test).