Figure 2.
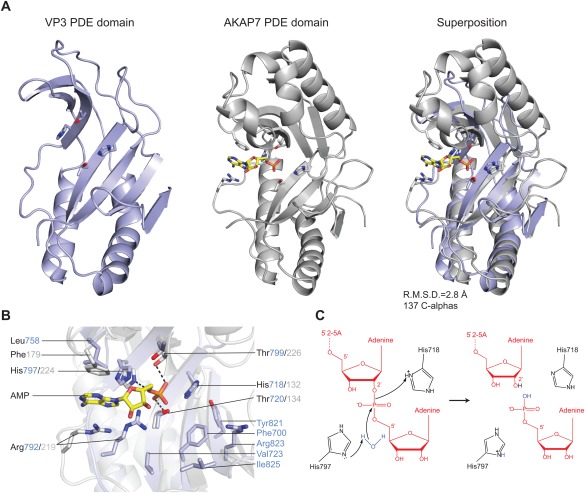
(A) Comparison of RVA VP3 (light blue) and human AKAP7 (grey, PDB ID 2FVK) phosphodiesterase domains. The structures were superimposed using the DALI server and are shown in identical orientations. The catalytic His and Thr residues as well as bound AMP ligand in AKAP7 are shown in stick representation. The AMP molecule is colored yellow. (B) Zoomed‐in view of the overlaid catalytic centers of the PDE domains of VP3 and AKAP7. Catalytic and substrate binding residues are shown as sticks and colored as in (A). Hydrogen bond interactions are depicted as dashed lines. (C) Proposed model for the 2′,5′‐phosphodiesterase catalytic mechanism of VP3. The side‐chain of His797 acts as a general base to abstract a proton from a water molecule, promoting the nucleophilic attack on the phosphate group. His718 acts as a general acid to donate a proton to the 2′‐oxygen of the leaving group. The 2′–5′‐oligoadenylate substrate is depicted in red.
