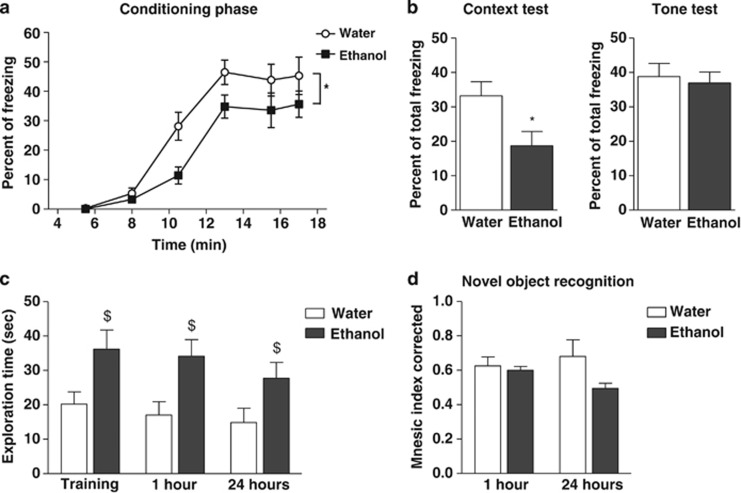
Figure 3.
Effects of ethanol intake on contextual fear memory and object recognition. (a, b) Cued and contextual fear memory was evaluated using the fear conditioning test. (a) Freezing was measured for each conditioning stimulus given to the mice followed by an intertrial interval. Points represent percent of freezing in function of the time. Each point is the mean±s.e.m. of n=6 (water) and n=9 (ethanol) mice; *P<0.05, repeated measures two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). (b) Percent of total freezing during the contextual test and the tone test is represented. Each bar is the mean±s.e.m. of n=6 (water) and n=9 (ethanol) mice; *P<0.05, Student's t-test. (c, d) Mnesic index was evaluated in the novel object recognition test. (c) Time spent exploring the objects was quantified during the acquisition and within the testing sessions 1 and 24 h post trial. Each bar is the mean±s.e.m. of n=5 (water) and n=8 (ethanol) mice; $P<0.05, repeated measures two-way ANOVA. (d) Mice recognition performances were represented as the corrected mnesic index for the new object. Each bar is the mean±s.e.m. of n=5 (water) and n=8 (‘ethanol') mice; *P<0.05, Bonferroni's multiple comparison test.