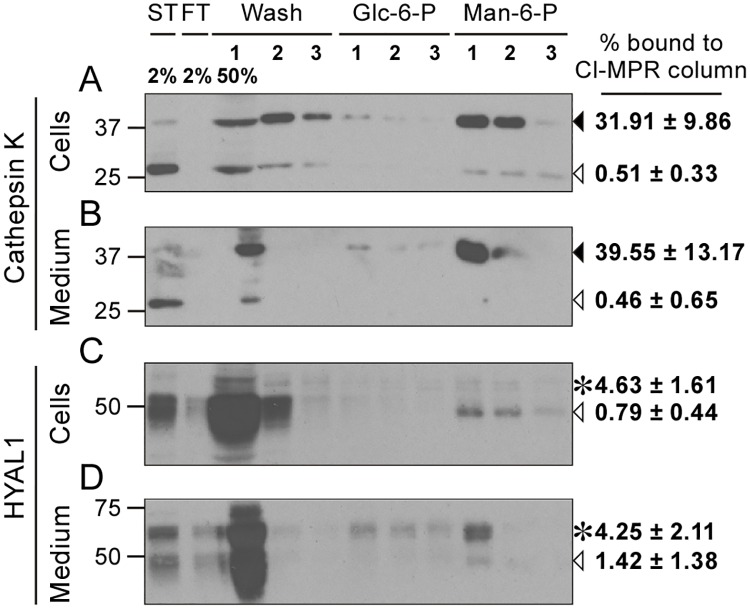
Fig 6. HYAL1 is poorly mannose 6-phosphorylated in osteoclasts.
Cell lysate (A, C) or culture medium (B, D) of osteoclasts differentiated from RAW264.7 cells were collected after a 5 h culture period in serum-free conditions and loaded on a CI-MPR affinity column. The presence of cathepsin K (A-B) and HYAL1 (C-D) was analyzed, using western blotting (reducing conditions), in the starting sample (ST), flow-through (FT), washes (Wash) and elution fractions (trichloroacetic acid-precipitated). Proteins non specifically bound to the column were eluted using 5 mM of Glucose 6-Phosphate (Glc-6-P) while proteins that bound specifically to CI-MPRs were eluted with 5 mM of mannose 6-phosphate (Man-6-P). Cathepsin K precursor and cleaved forms are indicated by closed and open arrowheads, respectively. The 65 kDa precursor and 48 kDa mature forms of HYAL1 are indicated by asterisks and open arrowheads, respectively. One representative experiment is shown. Specific binding of each cathepsin K or HYAL1 forms to the column was calculated in n = 3 independent experiments and expressed as a percentage of the total signal detected for the corresponding form in the starting sample (mean ± SD of the 3 independent experiments are shown).