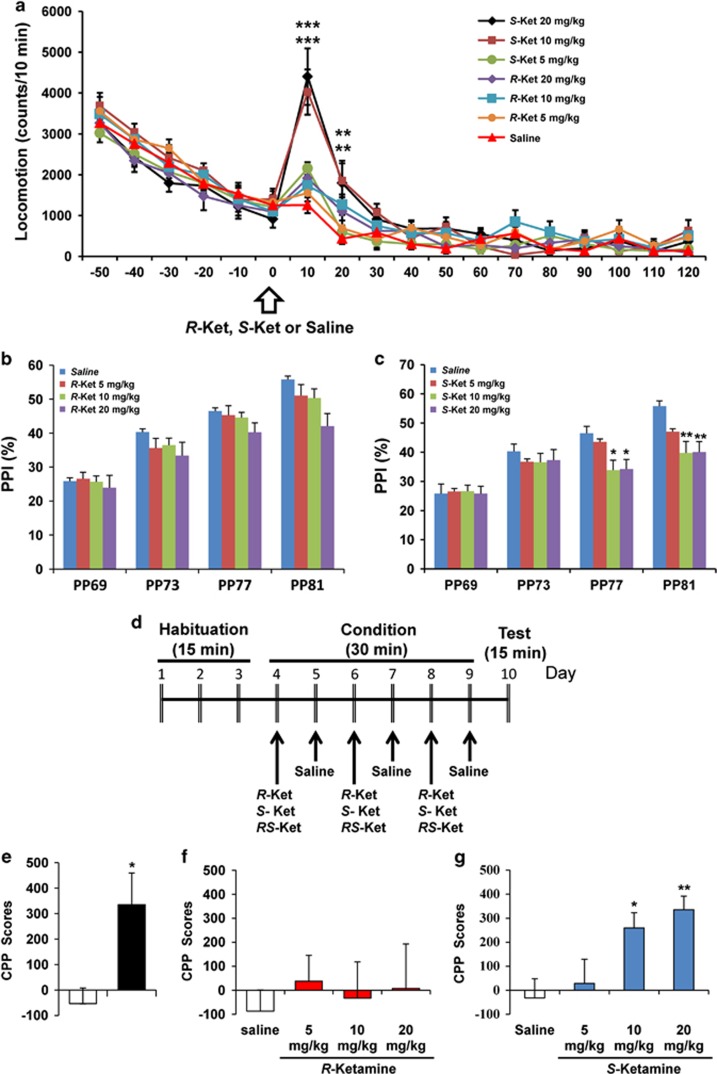
Figure 5.
Side-effect profiles for S-ketamine, but not R-ketamine, in mice. (a) Effects of R-ketamine and S-ketamine on locomotion in control mice. One hour after habituation, saline, R-ketamine (5, 10 or 20 mg kg−1) or S-ketamine (5, 10 or 20 mg kg−1) was administered intraperitoneally into mice. Two-way ANOVA analysis revealed significant interactions (drug: F6,125=6.441, P<0.001; time: F17,125=138.838, P<0.001; interaction (drug × time): F102,1125=2.814, P<0.001). Values represent the mean±s.e.m. (n=8). **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 compared with the saline-treated group. (b) Effects of R-ketamine (5, 10 or 20 mg kg−1) on PPI test in control mice. The MANOVA revealed no significant effect (Wilks' lambda=0.713, P=0.333). Values represent the mean±s.e.m. (n=8). (c) Effects of S-ketamine (5, 10 or 20 mg kg−1) on the PPI test in control mice. The MANOVA revealed significant effect (Wilks' lambda=0.554, P=0.019). Values represent the mean±s.e.m. (n=8). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 compared with the saline-treated group. (d) The schedule of CPP model and behavioral tests after treatment. (e) RS-ketamine (10 mg kg−1) significantly (P=0.0125) increased CPP scores in mice (n=9). *P<0.05 compared with the saline-treated group. (f) R-ketamine (5, 10 or 20 mg kg−1) did not increase CPP score (F3,35=0.147, P=0.931). (g) S-Ketamine (5, 10 or 20 mg kg−1) significantly increased CPP score (F3,34=5.441, P=0.004). Values represent the mean±s.e.m. (n=9–10). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 compared with the saline-treated group. ANOVA, analysis of variance; CPP, conditioned place preference test; MANOVA, multivariate analysis of variance; PPI, prepulse inhibition.