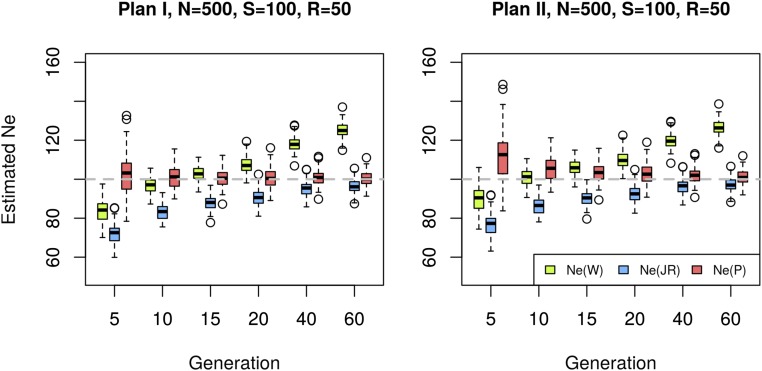
Figure 2.
Effective population size estimated with different methods. Sixty generations of Wright–Fisher neutral evolution with diploid individuals were simulated for n = 2000 unlinked loci (SNPs). Prior to sampling, the population was increased to a census size of individuals at each generation. At the starting population and at each indicated time point a sample was taken to create a pool of individuals. The pool was sequenced to an average coverage of and was estimated on the resulting data set by separately contrasting allele frequencies at generation 0 to each of the evolved generations denoted on the x-axis, using (Waples 1989), and (Jorde and Ryman 2007). Each box represents results from 100 simulations with identical parameters. The dashed gray line shows the true value of Data are simulated under plan I assumptions and the results of plan I and II estimators are shown in the left and right panels, respectively.