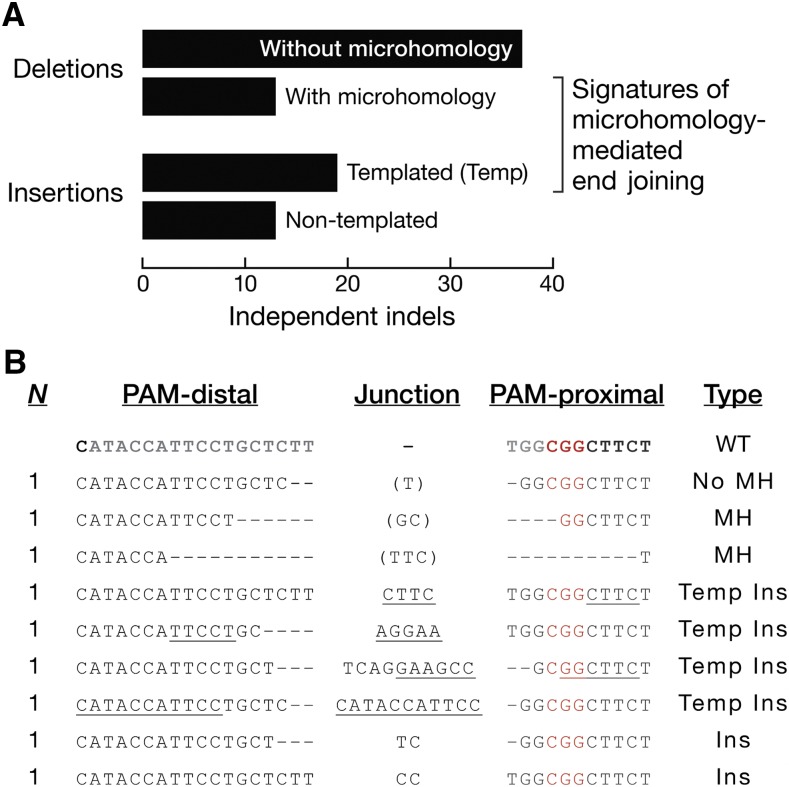
Figure 3.
Indel junctional signatures suggest the involvement of microhomology-mediated end joining. (A) Eighty-two independent indels at seven DSBs (Tables S1–S6 in File S1) were classified as deletion without microhomology when there was ≤1 nt of microhomology; as deletion with microhomology when there were ≥2 nt of microhomology; as templated insertion when there were ≥3 nt of inserted nucleotides with identifiable template; or as nontemplated insertion when nucleotide insertions were present without an identifiable template. (B) Indels at the white sgRNA-1 target site. The 20 nt sgRNA target sequence is in gray. The PAM sequence is in red. The DSB junction is 3 bp away from the PAM. Dash: deleted nucleotide. Underline: templated insertions at the junction. Nucleotides in parentheses identify microhomologies that can be mapped to either the PAM-distal or PAM-proximal side of the DSB. G0 embryos were vas-Cas9, Lig4169. Ins, nontemplated insertion; MH, deletion with microhomology; N, number of independent events; No MH, deletion without microhomology; Temp Ins, templated insertion; WT, wild type.