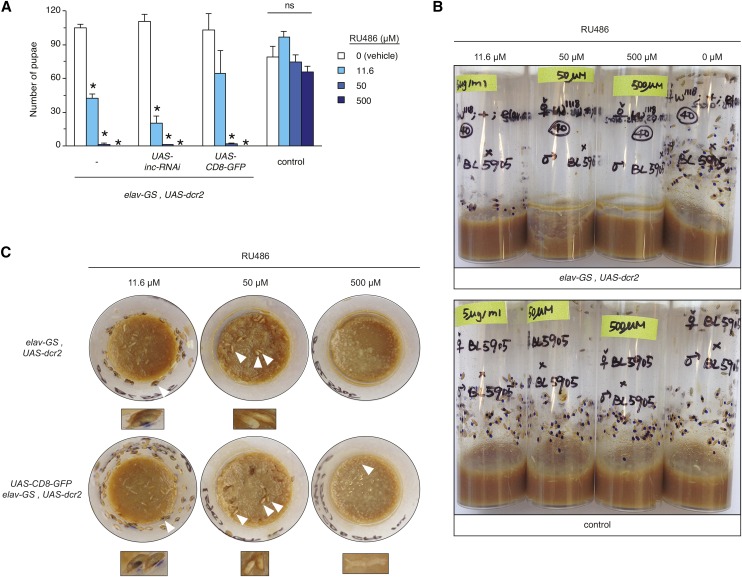
Figure 2.
Developmental RU486 exposure is toxic to elav-GS animals. (A) Pupal number is shown for indicated genotypes exposed developmentally to vehicle or to indicated RU486 concentrations. Mean ± SEM is shown; * P < 0.01, and ns denotes P > 0.05, for comparisons to vehicle control within each genotype. Data are averaged from two independently derived elav-GS, UAS-dcr2 recombinant lines. (B and C) Side view (B) and top-down (C) photographs of vials containing progeny of indicated genotypes. Photographs were taken 11 d after crosses were initiated. Pupal cases are marked with blue dots to facilitate counting and to distinguish them from adults that have eclosed. In (C), white arrowheads indicate mature pigmented pupae on vial walls (11.6 µM RU486), immature unpigmented pupae located on the food surface (50 µM), and undeveloped eggs and embryos (500 µM). Magnifications are shown underneath top-down photographs.