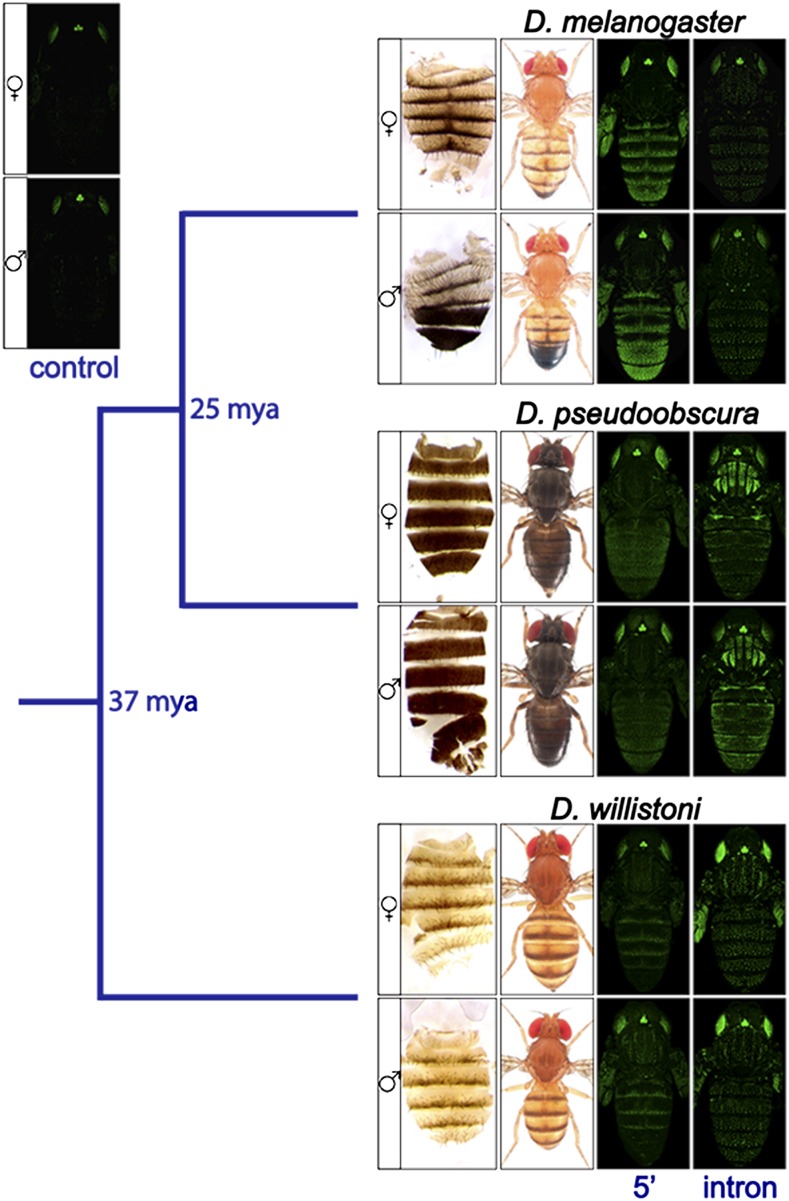
Figure 1.
Differences in adult pigmentation patterns correlate with differences in yellow expression patterns between Drosophila species. Phylogenetic relationship between three species from the Sophophora subgenus, D. melanogaster, D. pseudoobscura, and D. willistoni, are shown. For each species, panels are as follows: from left to right, dissected dorsal abdomen, dorsal view of adult fly, pupal GFP expression in a D. melanogaster host driven by 5′ intergenic sequence upstream of yellow, pupal GFP expression in a D. melanogaster host driven by yellow intronic sequence, with females shown in the top row and males shown in the bottom row. Images of dorsal view of adult flies are courtesy of Nicolas Gompel. The panel labeled “control” shows pupal GFP expression in females (top) and males (bottom) driven by only the basal promoter used to construct all other reporter genes. The GFP used in these constructs is a nuclear enhanced green fluorescent protein (nEGFP). Additional information about these reporter genes can be found in Kalay and Wittkopp (2010), in which these images of adult flies and GFP expression patterns were first published.