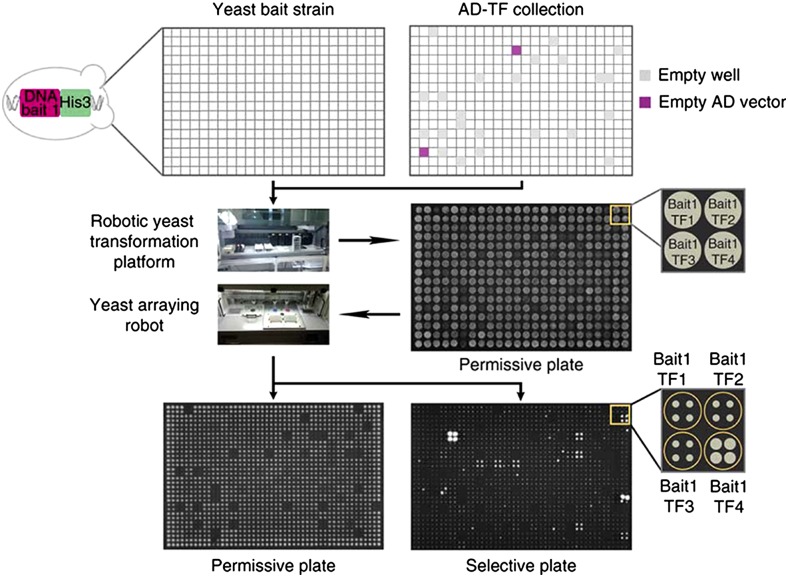
Figure 3.
Overview of high-throughput Y1H assay. Each yeast strain with a yellow enhancer fragment (DNA bait)-HIS3 reporter construct integrated into its genome (Yeast bait strain) was transformed with a library of transcription factors (TFs) fused to a Gal4 activation domain (AD-TF collection) using 384-well plates. As negative controls, each TF plate contained empty wells (gray squares in AD-TF collection plate) as well as constructs with activation domains (AD) without a TF attached (magenta squares in AD-TF collection plate) to test for activation in the absence of a TF. Then, each “bait-TF” combination was quadruplicated using a yeast arraying robot, first onto a permissive plate (no 3AT), then onto selective plates with increasing amounts of 3AT. After 3 d of growth, the permissive plate (no 3AT) was imaged as a reference. After 7 and then 10 d of growth, the selective plates were imaged and colony growth was scored as a readout of DNA bait–TF interaction. This figure is modified from Hens et al. (2011).