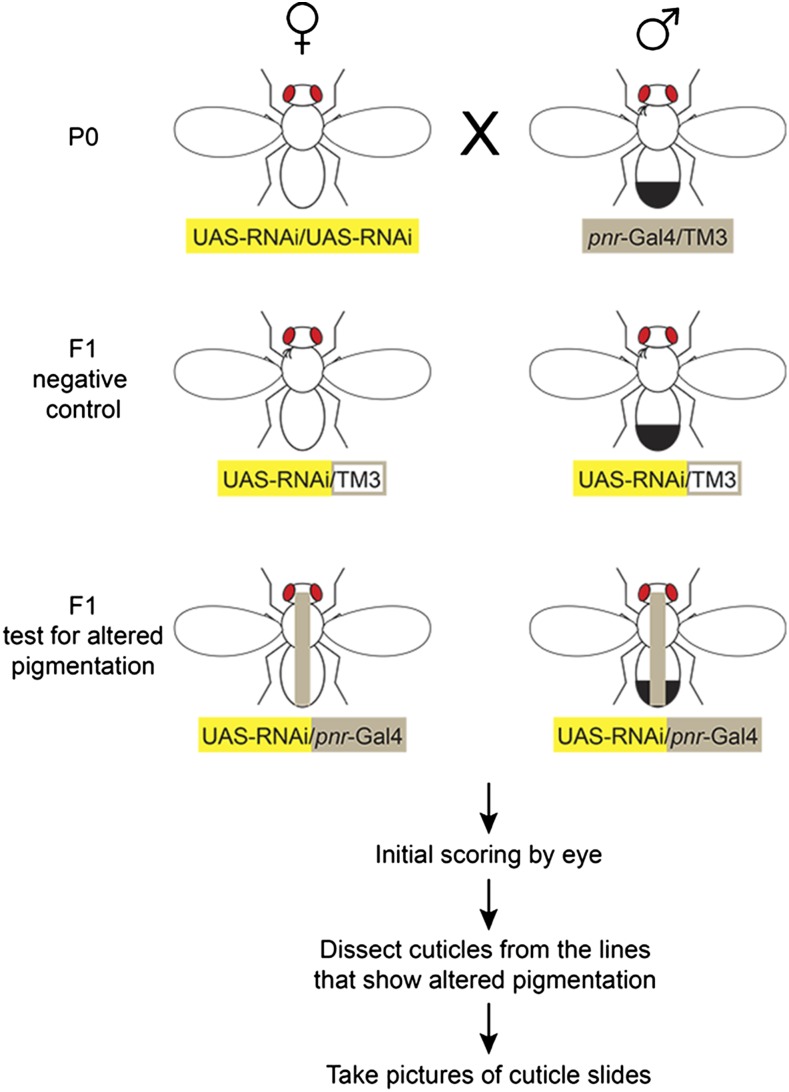
Figure 4.
Overview of RNAi screen for transcription factors affecting pigmentation in D. melanogaster. To determine whether a given TF affects abdominal pigmentation in D. melanogaster, one or more homozygous UAS-RNAi lines reducing activity of that TF were each crossed to a line heterozygous for the pannier-Gal4 (pnr-Gal4), which drives expression in the dorsal midline (gray stripe), and a TM3 balancer on the 3rd chromosome (P0 cross). Half of the F1 progeny inherited the UAS-RNAi construct and the TM3 balancer (control), whereas the other half inherited the UAS-RNAi construct and the pnr-Gal4 driver (knockdown). The presence or absence, respectively, of a bristle phenotype on the humeral (shoulder) region of adult flies caused by a mutation on the TM3 balancer chromosome was used to distinguish control and knockdown flies. After scoring initially for possible abdominal pigmentation differences by eye, cuticles were dissected from lines that showed potentially altered abdominal pigmentation. Dissected cuticles were mounted on microscope slides and imaged as described in Materials and Methods.