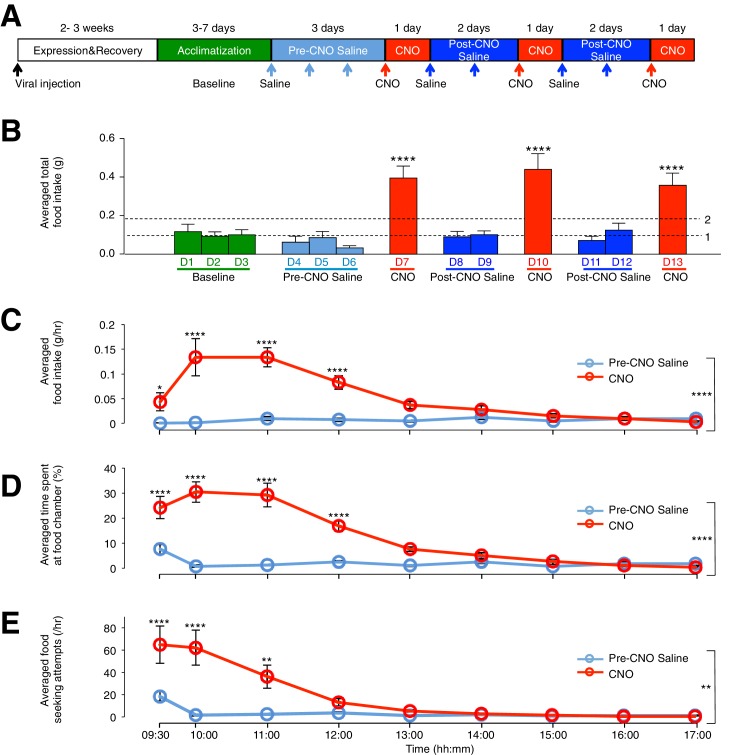
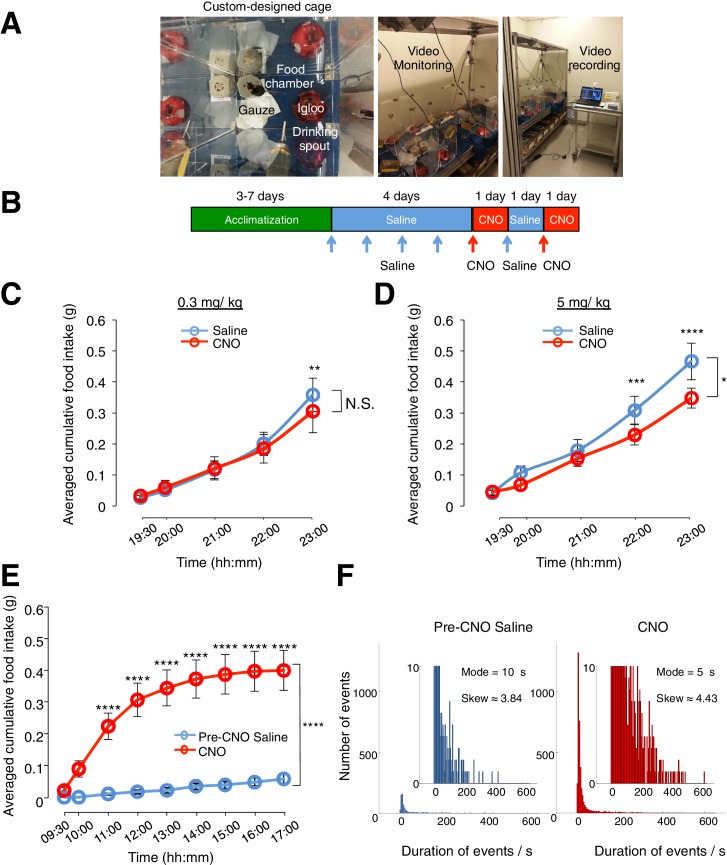
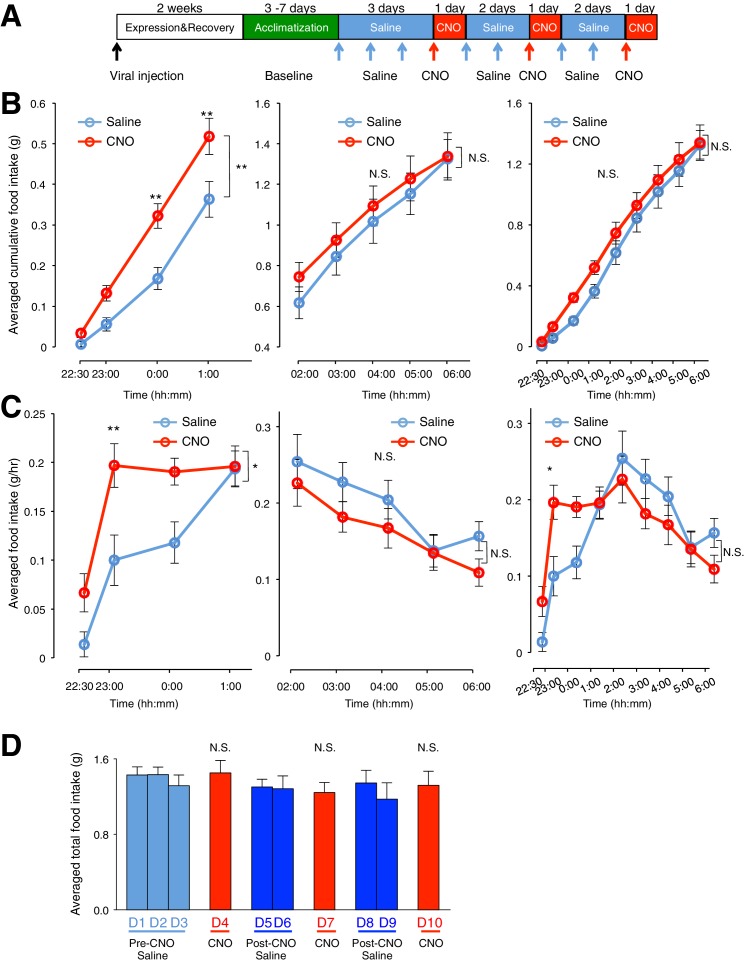
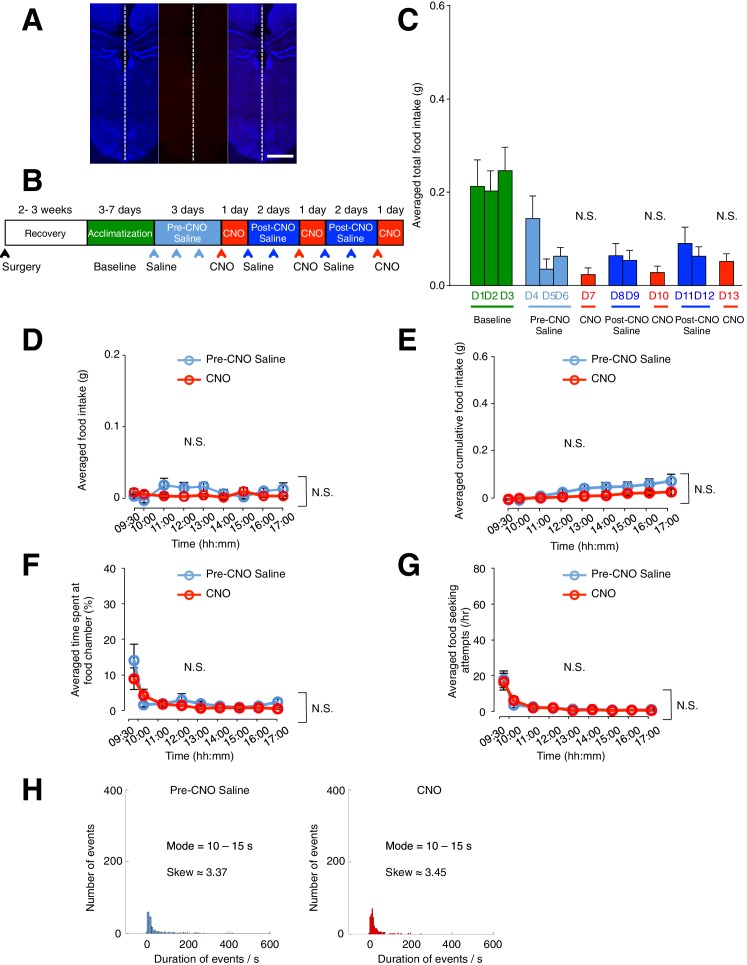
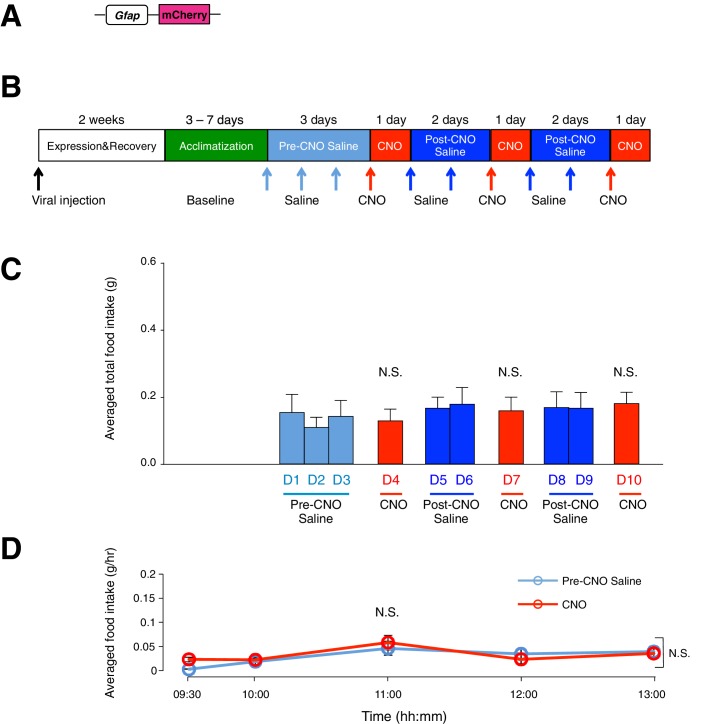
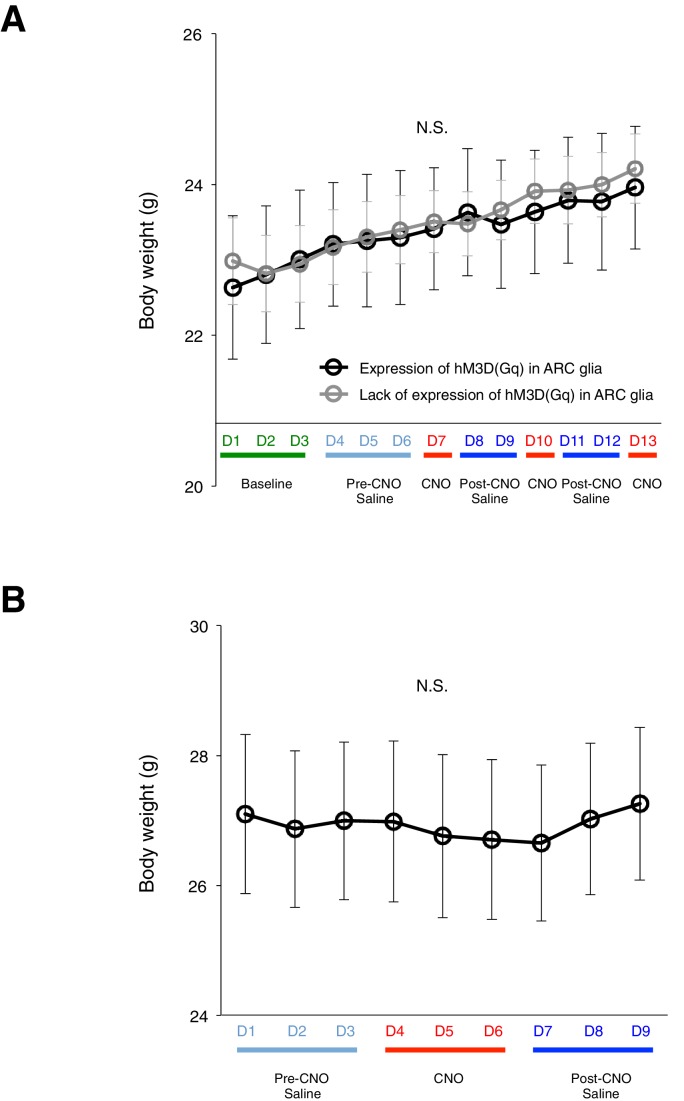
Figure 2. CNO-dependent activation of hM3D(Gq)-mCherry expressing ARC glia evokes increased day food intake, time spent at food chamber and food seeking attempts in C57BL/6 mice.
(A) Schematic of experimental paradigm. The mice were allowed to recover and for hM3D(Gq)-mCherry to be expressed 2–3 weeks post viral injection before acclimatization in custom cages for 3–7 days (baseline) and to saline injection for three days (pre-CNO saline). CNO injections were repeated for three days, each separated by two days of saline injection (post-CNO saline) to allow the CNO effects to clear. All injections were performed at 09:00 while the food intake was measured at specific time points between 09:00–17:00. All mice were housed in custom cages between 09:00–17:00 and returned to the standard cages after 17:00 daily. (B) Total food intake between 09:00–17:00 during baseline, pre-CNO saline, CNO and post-CNO saline averaged across animals. Dotted line 1 refers to the averaged total food intake across baseline, pre- and post- CNO saline while dotted line 2 refers to two folds of this average. (C) Food intake during hourly time points from 09:00 to 17:00 (except from 09:00–09:30 and 09:30–10:00 where 30 min time points were used) during pre-CNO saline and CNO administration. (D) The percentage of time mice spent at food chamber relative to other cage areas during specific time points following pre-CNO saline and CNO administration. (E) The frequency of attempts made to access the food chamber during specific time points following pre-CNO saline and CNO administration. In Figure 2C–E, values between 09:00–09:30 and 09:30–10:00 were normalized to hourly values. Pre-CNO saline and CNO values were averaged across three days of repeats before computing the average across animals. Two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc tests was used. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ****p<0.0001. Error bars represent SEM. See also Figure 2—figure supplements 1–6.