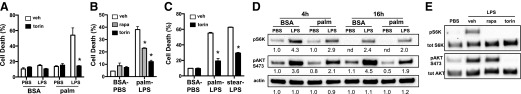
Figure 1. mTOR inhibitors protect macrophages from lipotoxic cell death.
(A) pMACs were treated with 250 μM palmitate (palm) or BSA ± 50 ng/ml LPS in the presence of vehicle (veh; white bars) or 100 nM torin (black bars), and cell death was assessed by annexin-PI flow cytometry. (B) pMACs were incubated with BSA-PBS or palm-LPS in the presence of veh (white bars), 100 nM rapamycin (rapa; gray bars) or 100 nM torin (black bars), and cell death was determined by 30 h via annexin-PI flow cytometry. (C) Macrophages were stimulated with palm-LPS or stearate (stear; 100 μM)-LPS in combination with veh or torin, and cell death was quantified by annexin-PI flow cytometry. (D) Kinetic analysis of S6K and AKT phosphorylation by Western blotting under the indicated conditions. (E) pMACs were stimulated with PBS or LPS for 4 h in presence of veh, rapa, or torin, and S6K and AKT phosphorylation was assessed by Western blotting. Densitometric quantification of the bands is shown beneath the blot. nd, not determined. Bar graphs report means ± se for a minimum of 3 experiments, each performed in triplicate. *P < 0.05 for veh vs. inhibitor.