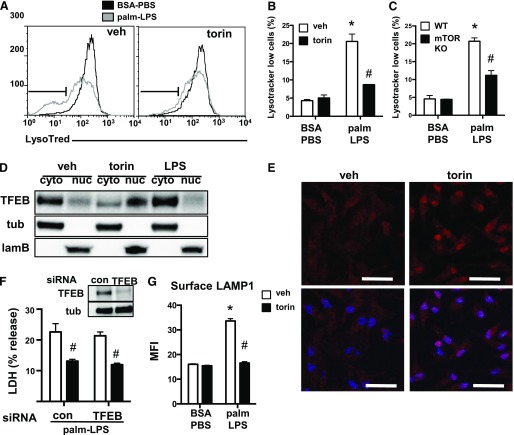
Figure 7. TFEB is not required for the protective effect of torin on lipotoxic macrophage cell death.
(A) pMACs were stimulated with BSA-PBS or palm-LPS in the presence (right) or absence (left) of torin, and lysotracker red staining was assessed by flow cytometry. Lysotracker red low cell population is defined by the gate shown in black. (B and C) Bar graph quantification lysotracker red low staining cells from WT macrophages treated with vehicle (veh) or torin (B) or macrophages from mTOR flx/flx Cre negative vs. mTOR flx/flx LysM-Cre double-positive (mTOR KO) mice (C). (D) pMACs were treated with veh, torin, or LPS for 2 h, after which protein was isolated and cytosolic (cyto) vs. nuclear (nuc) fractionation was performed. TFEB distribution and fractionation controls [tubulin (tub) for cytosol, laminin B (lamB) for nucleus] were assessed by Western blotting. (E) Cells were treated with veh or torin for 2 h, after which they were stained with an antibody to TFEB (red) and imaged by fluorescence microscopy. Hoechst nuclear counterstaining (blue) is overlaid on TFEB staining in lower panels. (F) pMACs were transfected with control (con) or TFEB-specific siRNA pools and stimulated with palm-LPS ± torin. Degree of protein knockdown is shown in the figure inset. (G) The effect of torin on lysosome exocytosis was assessed by staining surface LAMP1 by using a fluorescently conjugated antibody on nonpermeablized cells, followed by flow cytometric quantification of mean fluorescence intensity (MFI). Bar graphs report means ± se for a minimum of 3 experiments, each performed in triplicate. *P < 0.05 for BSA-PBS vs. palm-LPS; #P < 0.05 for veh vs. torin. Scale bar, 75 μm.