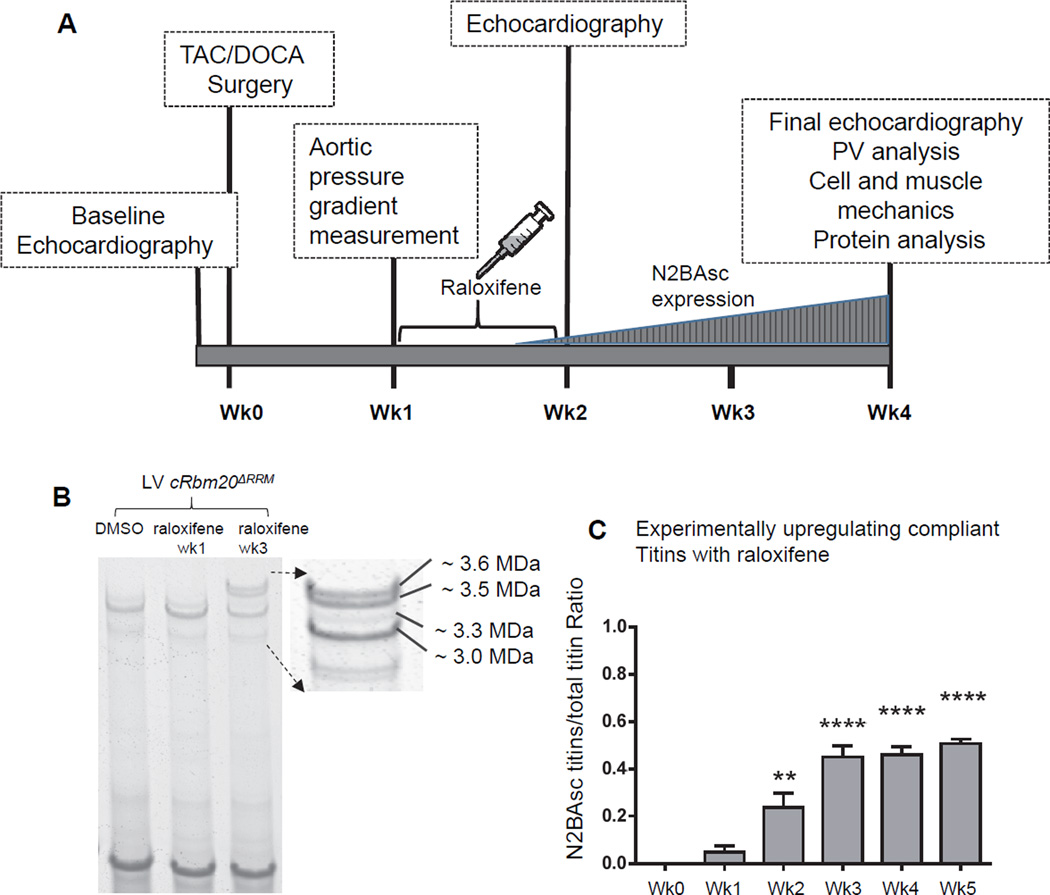
Figure 1.
A) Schematic of experimental protocol. Diastolic dysfunction was induced in cRbm20ΔRRM mice by TAC surgery with DOCA pellet implantation. At 1 week post TAC/DOCA surgery, post constrictional aortic flow velocity was measured to quantify severity of aortic constriction. Raloxifene or DMSO (vehicle) was then administered via intraperitoneal injection daily for 8 consecutive days. At 2 weeks post TAC/DOCA surgery, echocardiography was used to evaluate cardiac morphology and study diastolic dysfunction. At 4 weeks post-surgery, a final echo analysis was performed after which the animals were utilized for PV analysis, cell/muscle mechanics or protein studies. B) Titin isoform expression in cRbm20ΔRRM mice after raloxifene injection. A representative gel image shows that LV myocardium of cRBM20ΔRRM mice treated with raloxifene expressed the normal adult N2B titin (~3.0 MDa) and N2BA titin (~3.3 MDa) isoform at 1 week, but after 3 weeks also expressed 2 very large titin isoforms (~3.5 and 3.6 MDa in size) that we named super-compliant titin, or N2BAsc. C) A significant amount of N2BAsc titins was observed as early as 2 weeks after beginning of raloxifene injection. The ratio of N2BAsc / total titin reached ~ 0.45 after week 3 and then remained nearly stable. **p≤0.01, ****p≤0.0001 vs. Week 0. (n=10,5,6,6,6,4 mice for week 0,1,2,3,4,5 respectively).