Fig. 3.
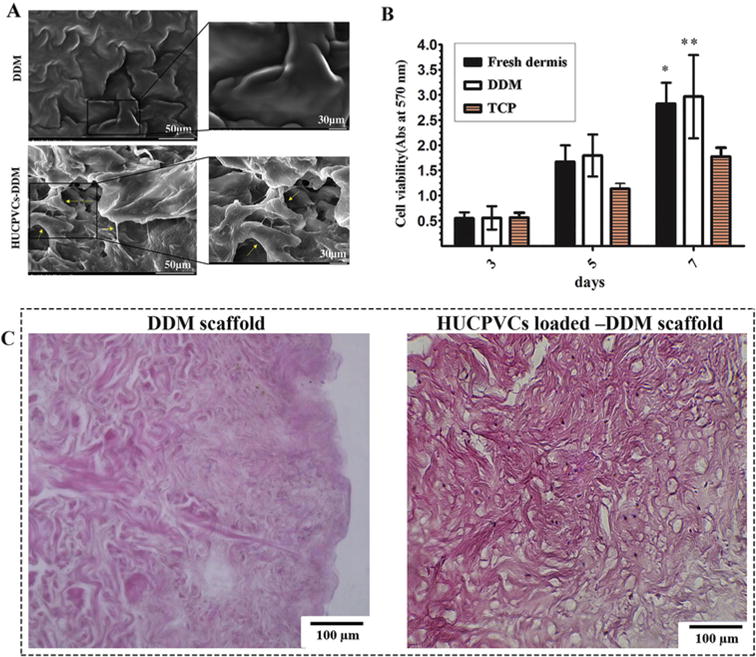
Cellular interaction of the DDM scaffolds with HUCPVCs. (A) Representative SEM micrographs of the DDM scaffold showing that the HUCPVCs cells were attached and distributed on the surface of the scaffolds after 5 days. The augmented cells attached to each other and to the surface of the DDM scaffolds. The extended lamellipodia of the HUCPVCs can be observed in the DDM scaffolds. (B) The MTT photograph revealed that there was a significant difference between the experimental groups and control group after 7 days. These results suggested that the DDM scaffolds promoted the HUCPVCs proliferation and had no cytotoxic effects. (P values of the fresh dermis group and DDM group are *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 respectively). (C) Histological evaluation of DDM scaffold and HUCPVCs loaded–DDM scaffold after 7 days in vitro culture.
