Fig. 5.
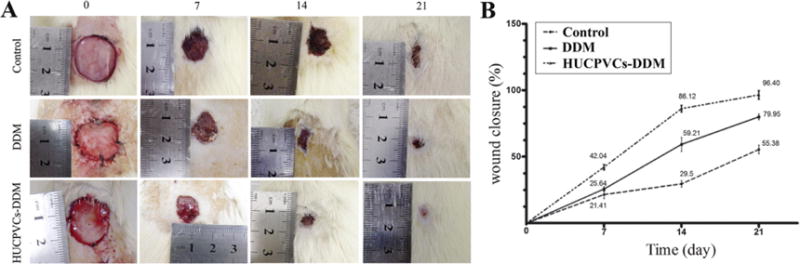
Wound healing effects of DDM alone and HUCPVCs loaded-DDM in a diabetic rat model of cutaneous wounds. (A) Representative photographs of the wound closure rate among the three groups at days 0, 7, 14 and 21 after grafting. (B) Quantitative analysis indicated that the wound size was reduced in the HUCPVCs loaded-DDM group compared with the control and DDM groups after 21 days (P < 0.001). The results showed that wound closure rate in the DDM group was higher than control group, and significant differences were observed at 7 and 14 days post-wounding (P < 0.001). The HUCPVCs loaded-DDM group demonstrated no significant improvement in wound healing compared with the DDM treated groups at 7 days. Moreover, the HUCPVCs loaded-DDM scaffolds had much higher wound healing rate and contraction ability than the other groups.
