Figure 1.
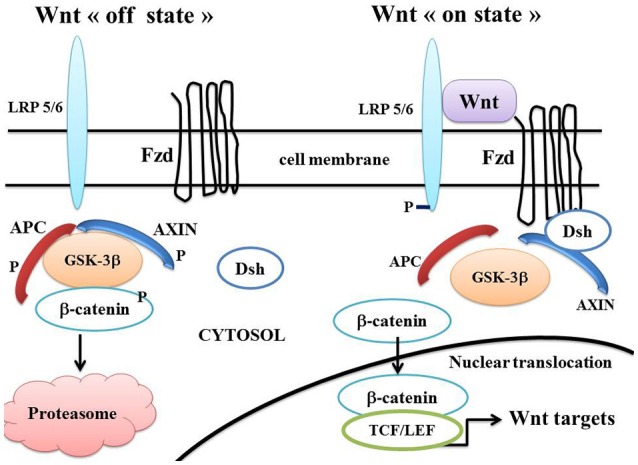
A schematic model of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. In the Wnt “on state” (right part), Wnt binds both Fzd and LRP5/6 receptors to initiate LRP phosphorylation as well as Dsh/Fzd internalization. Dsh membrane translocation leads to dissociation of the axin/APC/GSK-3β complex. Beta-catenin phosphorylation is inhibited and it accumulates in the cytosol. The cytosolic beta-catenin translocates to the nucleus and binds to TCF/LEF factors. This results in the Wnt-responsive gene transcription. In Wnt “off state” (left part), Dsh dissociates from Fzd and Axin. APC and axin complex with GSK-3β. Beta-catenin is phosphorylated, dissociates from GSK-3β, migrates to the cytosol and is destroyed in the proteasome. Abbreviations: APC, adenomatous polyposis coli; Dsh, Disheveled; Fzd, Frizzled; GSK-3β, glycogen synthase kinase-3beta; LRP5/6, low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5/6; TCF/LEF, T-cell factor /lymphoid enhancer factor.
