Figure 2.
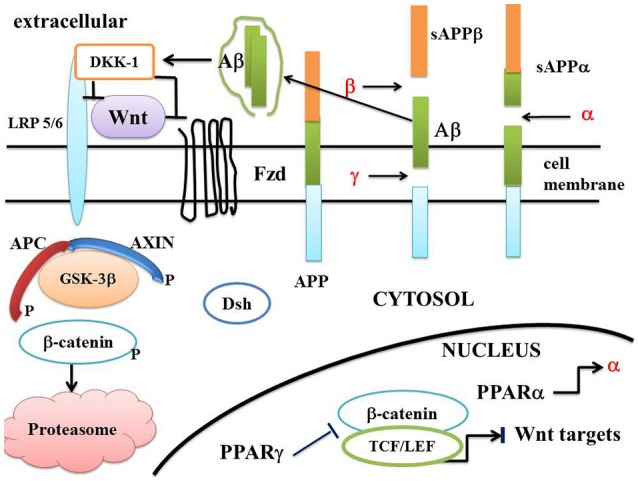
A schematic model of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in Alzheimer disease. In AD, the “on state” of canonical Wnt/beta-catenin pathway is interrupted at two potential levels. Firstly, extracellular Aβ activates DKK1 which inhibits the interaction between Wnt and LRP 5/6. Binding of Wnt to Fzd is suppressed and Dsh dissociates from Fzd/Axin and migrates to the cytosol. The recruitment of the destruction complex to the plasma membrane is suppressed. Inactivation of Dsh leads to stimulation of GSK-3β. Thus, APC and AXIN interact with GSK-3β and beta-catenin (Wnt “off state”). Beta-catenin is phosphorylated by GSK-3β. The destruction complex AXIN/APC/GSK-3β is activated and enhances the destruction process of beta-catenin in the proteasome. Secondly, PPAR gamma which is activated by agonists can inhibit the beta-catenin/TCF/LEF complex in the nucleus, thus inhibiting the transcription of Wnt target genes. Amyloid precursor protein (APP) can be cut into various fragments by α, β, and γ secretases. PPAR α activates the transcription of α secretase. Abbreviations APC, adenomatous polyposis coli; Dsh, Disheveled; Fzd, Frizzled; GSK-3β, glycogen synthase kinase-3beta; LRP5/6, low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5/6; TCF/LEF, T-cell factor /lymphoid enhancer factor; sAPPα, soluble APPα ectodomain; sAPPβ, soluble APPβ ectodomain; APP, Amyloid precursor protein; α, β, and γ, α, β, and γ secretases; Aβ, amyloid β peptide; DKK1, Dickkopf-related protein1.
