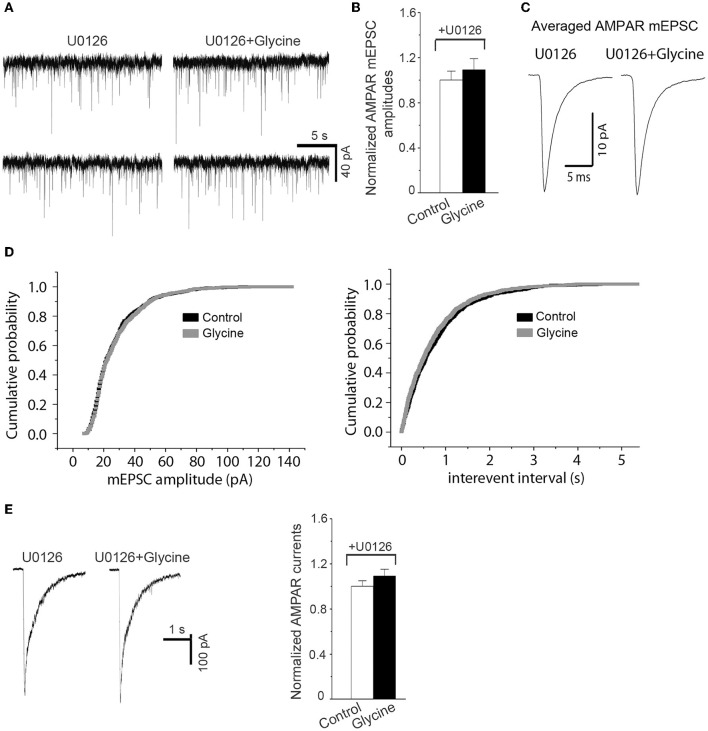
Figure 3.
Inhibition of ERK1/2 activation prevents potentiation of AMPAR function by glycine. (A) Representative AMPAR mEPSCs recorded before and 10 min after 1.0 min application of 100 μM glycine in cultured hippocampal neurons in which NMDARs and glycine receptors are inhibited. (B) Summarized data show that the enhancement of AMPAR mEPSCs by glycine is antagonized by pretreatment of ERK1/2 inhibitor U0126 (5.0 μM; n = 6). (C) Sample of averaged AMPAR mEPSCs from the neurons at present of U0126 before (881 events) and after (877 events) treatment of 100 μM glycine. (D) Cumulative probability plots of peak amplitudes and interevent intervals of AMPAR mEPSCs (bin size o.5 pA and 10 ms, respectively). (E) Left: Representative AMPAR whole-cell currents induced by AMPA (100 μM) recorded before and 10 min after treatment of 100 μM glycine in hippocampal neurons where NMDARs and glycine receptors are inhibited. Right: Summarized data show that the enhancement of AMPAR whole-cell currents by glycine was blocked by U0126 pretreatment (n = 8).