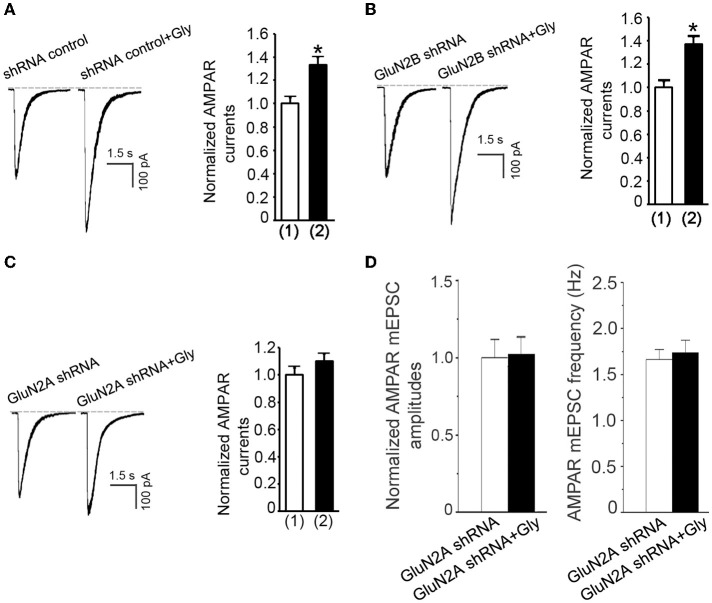
Figure 7.
Glycine enhances AMPAR function through metabotropic activity of GluN2ARs in hippocampal neurons. (A) Transfection of shRNA control does not influence glycine-induced potentiation of AMPAR currents in hippocampal neurons after NMDARs and glycine receptors are inhibited (n = 7, *p < 0.05). (1) shRNA control; (2) shRNA control + Gly. (B) GluN2B knockdown by GluN2B shRNA transfection does not influence glycine (100 μM) potentiation of AMPA-induced whole-cell currents in neurons where NMDARs and glycine receptors are inhibited (n = 7, p < 0.05). (1) GluN2B shRNA; (2) GluN2B shRNA + Glycine. (C) Knockdown of GluN2A by GluN2A shRNA transfection blocks glycine-induced potentiation of AMPAR currents in hippocampal neurons after NMDARs and glycine receptors are inhibited (n = 7). (1) GluN2A shRNA; (2) GluN2A shRNA+Gly. (D) Knockdown of GluN2A by GluN2A shRNA prevents glycine-induced increase in mean amplitude and mean frequency of AMPAR mEPSCs in hippocampal neurons after NMDARs and glycine receptors are inhibited (n = 6 for both all groups). Gly: glycine.