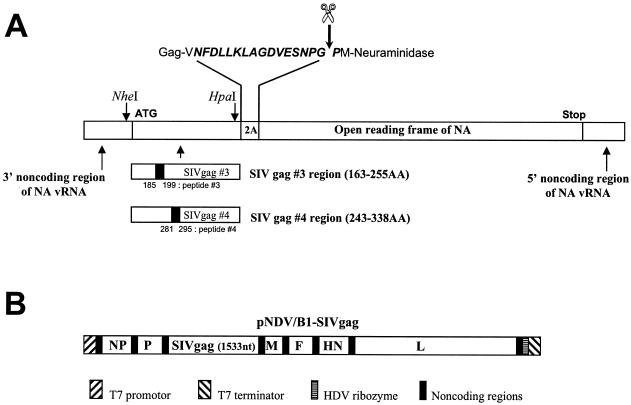
FIG. 1.
Recombinant viruses used in immunizations. (A) Schematic representation of Flu/SIVgag/2A/NA genes in rFlu/SIVgag viruses. rFlu/SIVgag viruses were constructed as described previously (31). Briefly, the SIV Gag-specific sequences were inserted in negative sense between the 3′ noncoding region of the neuraminidase (NA) gene and the protease recognition sequence 2A (NFDLLKLAGDVESNPGP) derived from foot-and-mouth disease virus by using NheI and HpaI restriction sites (41), and the corresponding genes were rescued into infectious influenza viruses. The expressed Gag-2A-NA polyprotein is cleaved into Gag-2A and NA polypeptides due to the autocatalytic activity of the 2A protease (44). However, it should be noted that recent evidence favors a mechanism of action of 2A due to “ribosomal skip” rather than to proteolytic self-cleavage (12). Peptides 3 and 4 within the Gag antigens used in the ELISPOT assays are also indicated. These two peptides were previously found to contain an epitope recognized by CD8+ T cells in BALB/c mice (31). (B) Schematic representation of pNDV/B1-SIVgag used to rescue rNDV/SIVgag. The pNDV/B1-SIVgag construct was made by inserting the SIV Gag gene into the unique XbaI cloning site (nucleotide 3163) located between the P and M genes of the original pNDV/B1 clone (30). The inserted gene contains the gene end, intergenic, and gene start sequences (5′-TTAGAAAAAATACGGGTAGAA-3′) required for expression of SIV Gag as a new transcriptional unit by the NDV RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. In addition, seven nucleotides (5′-CGCCACC-3′) were inserted upstream of the SIV Gag initiation site to introduce an optimal Kozak sequence (24). The final length of the encoded NDV genome was divisible by six. The indicated plasmid regions are not to scale.