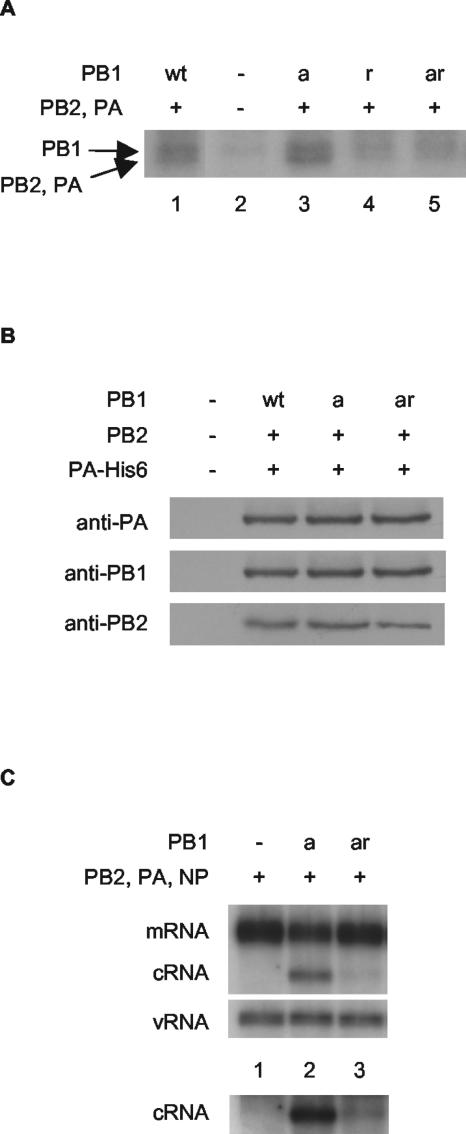
FIG. 4.
cRNA rescue is reduced by a mutation inhibiting the cRNA promoter-binding activity of PB1. (A) Substitution of tyrosine at residue 559 in PB1 or PB1a with alanine inhibits photochemical cross-linking of the polymerase complex to labeled cRNA. Partially purified His-tagged polymerase from cells transfected with plasmids expressing wild-type or mutant PB1, PB2, and PA-His6 (8), or empty vectors, as indicated, were cross-linked with a 32P-labeled RNA probe corresponding to the 3′-end cRNA in the presence of an excess unlabeled 5′-end cRNA by UV irradiation (8). The products were analyzed by 8% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and autoradiography. The positions of the PB1 and comigrating PB2 and PA cross-linked bands are shown. (B) The Y559A mutation in PB1 does not inhibit polymerase complex formation. Partially purified His-tagged polymerase from cells transfected with plasmids expressing wild-type or mutant PB1, PB2, and PA-His6 (8), or empty vectors, as indicated, was subjected to Western blotting with antibodies raised against the individual subunits as shown. (C) PB1-Y559A severely restricts cRNA rescue. 293T cells were transfected with plasmids expressing viral proteins (+) or empty plasmid vector (−), as indicated, 12 to 14 h prior to infection by A/WSN/33 virus in the presence of 100 μg of cycloheximide/ml. RNA was harvested at 2 h postinfection, and viral RNA species were analyzed by NA gene-specific primer extension assays. A longer exposure of the cRNA-specific bands is shown below to emphasize the differences in cRNA levels. wt, wild type; PB1a, PB1-D445A/D446A; PB1r, PB1-Y559A; PB1ar, PB1-D445A/D446A/Y559A.