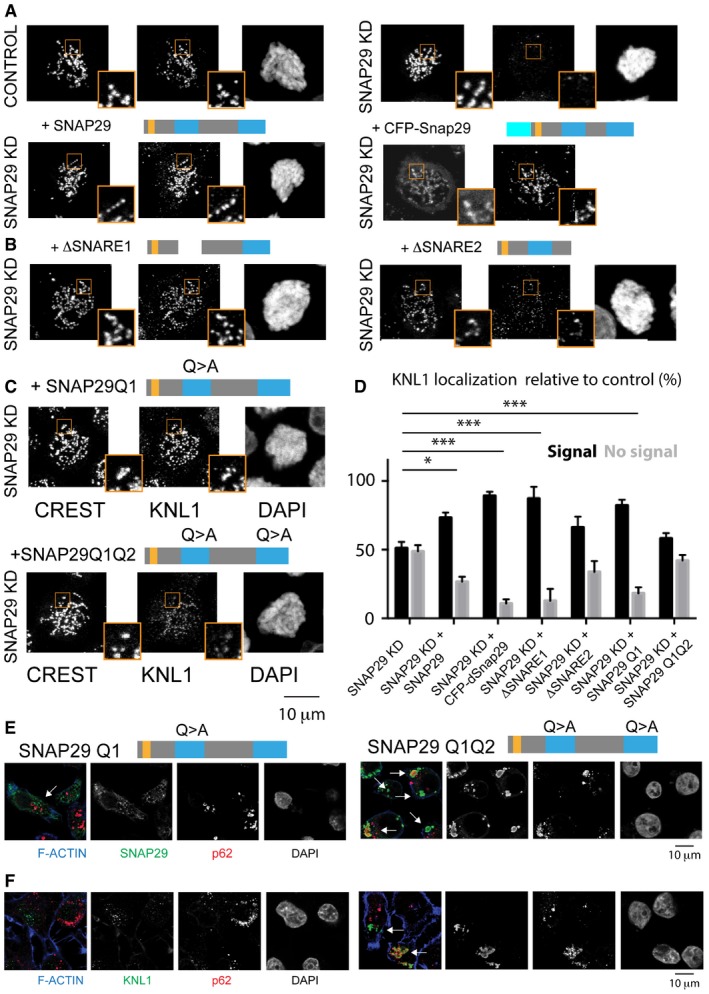
Figure 6. Snap29 mutants prevent recruitment of KNL1 to KTs and cause its ectopic accumulation.
-
A–CKNL1 localization analysis in control, SNAP29 KD, and SNAP29 KD expressing full‐length human SNAP29, CFP‐tagged, full‐length Drosophila Snap29 (CFP‐Snap29), or the mutant forms schematized above the panels. Max projections of single cells in prophase are shown.
-
DQuantification of three independent experiments evaluating the localization of KNL1 relative to CREST. 200 KTs from 10 control cells and 200 KTs from 10 SNAP29 KD cells per sample were identified by CREST staining. The mean with standard error of the mean (SEM) is shown, and P‐values are obtained by two‐way ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple comparison analysis relative to localization of KNL1 in SNAP29KD cells. *P ≤ 0.05; ***P ≤ 0.001
-
E, FSingle confocal sections of HeLa cells in interphase overexpressing the indicated constructs. In cells expressing SNAP29 Q1 Q2, SNAP29 (E) and KNL1 (F) accumulate in large compartments that are often positive for p62 (arrows).
