Figure 4. DIS3L2 targets short uridylated transcripts originating from mRNA transcription start sites.
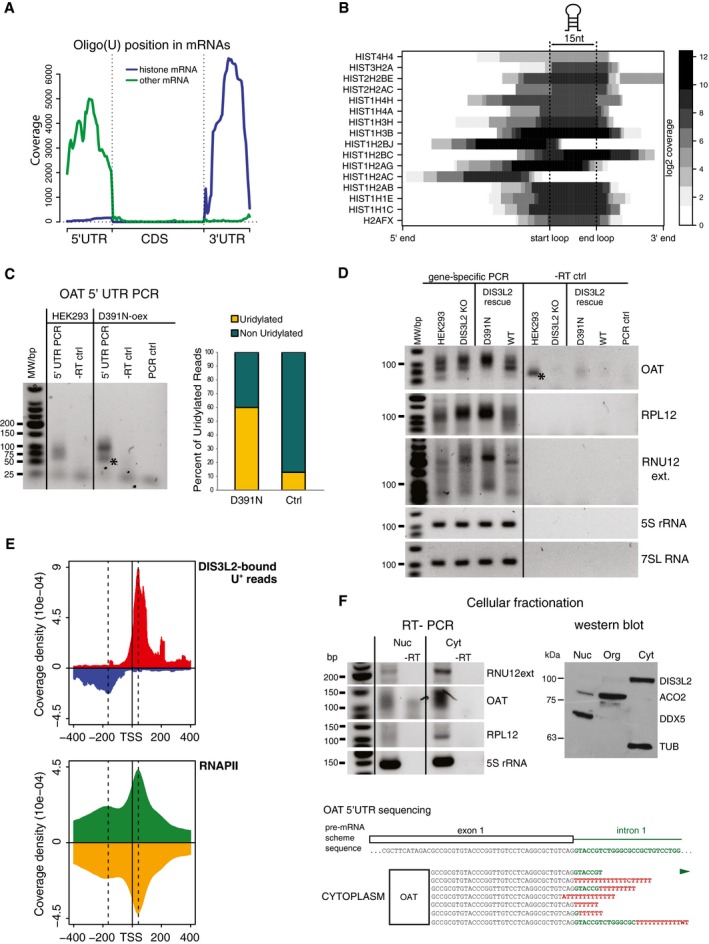
- DIS3L2‐bound uridylated mRNA reads map to the 5′ and 3′ UTRs.
- Most 3′ UTR U+ reads match the stem‐loop structure of histone mRNAs. Heat map representation of the uridylation position.
- The uridylated aberrant RNAs are stabilized in cells with non‐functional DIS3L2. Small RNAs were modified with 3′‐end linker, and linker‐specific primer was used for cDNA synthesis. Uridylated RNAs were PCR amplified in a semiquantitative way with the same amount of input RNA used for the RT reaction. We used a combination of the gene‐ and linker‐specific primers, −RT ctrl is RT–PCR control, where no reverse transcriptase was added; PCR control is a reaction with no cDNA added. The graph on the right summarizes the percentage of uridylated and non‐uridylated 5′ fragments of OAT mRNA in HEK293T‐Rex cells (Ctrl) and cells overexpressing mutant DIS3L2 (D391N). Bands marked with * are unspecific primer–dimer PCR products.
- DIS3L2‐bound uridylated RNAs are degraded by DIS3L2 in vivo. RT–PCR amplification of 5′ mRfs of OAT and RPL12 genes and 3′‐extended forms of U12 snRNA (RNU12 ext) from HEK293T cell lines with modified expression of DIS3L2 (as marked on top) was performed as described in (C). Regions of mature 5S rRNA and 7SL RNA were used as loading controls. DIS3L2 KO is a DIS3L2 knockout cell line. DIS3L2 rescue is DIS3L2 KO cells with stably integrated mutant (D391N) and wild‐type (WT) DIS3L2 expressing constructs, respectively. Bands marked with * are unspecific primer–dimer PCR products.
- Metagene analysis of the position of DIS3L2 D391N clipped U+ reads peak maximum around mRNA transcription start sites (TSS) and of the ChIP‐seq data for RNAP II.
- U+ 5′ mRfs and aberrant forms of U12 snRNA are highly enriched in the cytoplasm. RT–PCR detection of 5′ mRfs of the OAT and RPL12 and aberrant form of U12 snRNA was performed as described in (C) with RNA isolated from nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions, respectively. The RT–PCR amplification of the body of 5S rRNA was used as a positive control for RNA isolation and RT reaction in both fractions. The identity and uridylation status of cytoplasmic OAT U+ 5′ mRfs was confirmed by sequencing (shown on the bottom). In red are untemplated nucleotides, in green region corresponding to the first intron of OAT pre‐mRNA. The efficiency of the subcellular fractionation was monitored by Western blot (right panel, WB). DDX5 is nucleoplasmic, ACO2 is mitochondrial, and DIS3L2 and TUBα are cytoplasmic markers.
Source data are available online for this figure.
