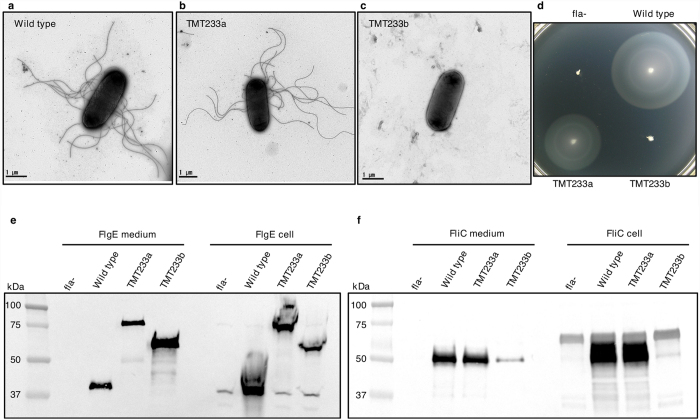
Figure 3. Flagellar biosynthesis for Salmonella strains producing a wild-type or hybrid FlgE hook protein.
Negatively-stained TEM images of whole cells of Salmonella strains: Wild type (a), TMT233a (b) and TMT233b (c), TMT233a encodes a hybrid hook protein, FlgEhyb1, with codons for the D3 and D4 domains of C. jejuni FlgE inserted into the flgE gene. TMT233b encodes a hybrid hook protein, FlgEhyb2, with codons for the D3 domain of C. jejuni FlgE inserted into the flgE gene. Six-hour swimming assay on 0.3% (w/v) agar-tryptone plates with wild-type S. enterica, TMT233a and TMT233b (d). Western blots showing levels of FlgE (e) and of FliC (f) exported into the culture medium and expressed in cells of the wild-type S. enterica, TMT233a and TMT233b. The MW of wild-type FlgE is 42 kDa, FlgEhyb1 is 84 kDa, FlgEhyb2 is 65 kDa and FliC is 52 kDa. “fla-” indicates the non-flagellated negative control, which was a flgE mutant strain bearing a tetRA insertion (TMTflgEtetRA).