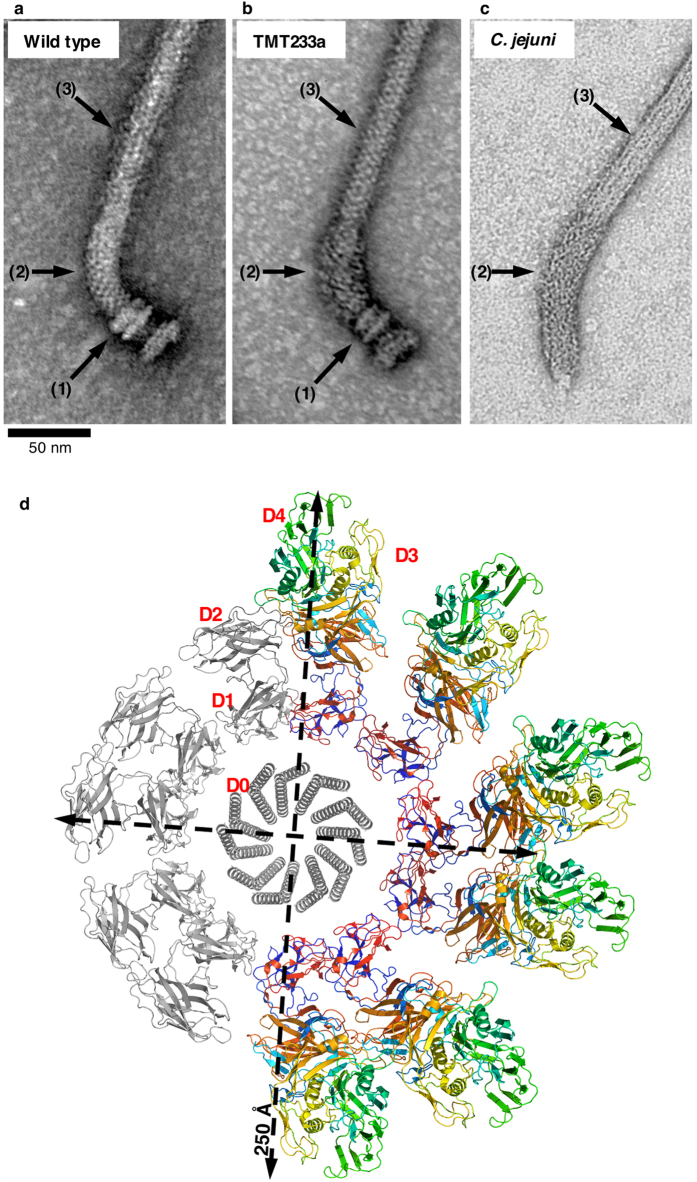
Figure 4. Transmission electron microscopy of purified flagella.
Negatively-stained TEM images of a flagellum from S. enterica strain SJW1103 (a), which is wild-type for flagellar biosynthesis, a flagellum from S. enterica strain TMT233a (b) and a flagellum from C. jejuni (c). The hook protein of strain TMT233a consists of the D0, D1, and D2 domains from S. enterica FlgE and the D3 and D4 domains inserted from C. jejuni FlgE; it therefore builds a flagellar hook that is similar to that of C. jejuni. The basal body, the hook, and the filament are indicated by arrows (1), (2) and (3), respectively. (d) Model in projection of the hook showing a single ring (11 molecules) of the hook based on the helical parameters of the hook from S. enterica. Five molecules in the ring, coloured in grey, are from FlgE of S. enterica while the six other molecules, colour-coded from the “N- to C-terminus” in rainbow colours, are from FlgE of S. enterica strain TMT233a.