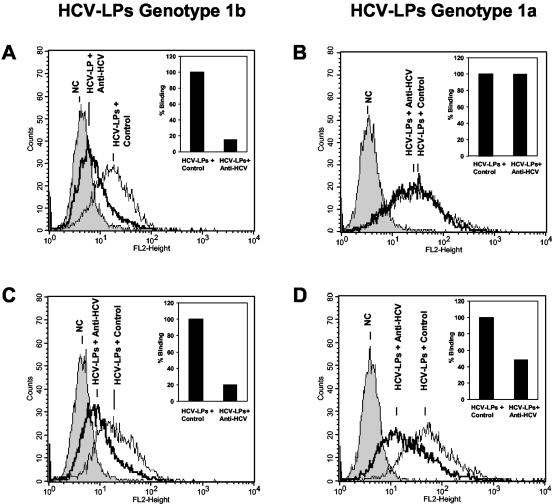
FIG. 4.
Strain-dependent inhibition of cellular HCV-LP binding. For the assessment of antibody-mediated neutralization of binding, HCV-LPs derived from the HCV-J strain (genotype 1b) (A and C) or clone H77c (genotype 1a) (B and D) were incubated in subsaturating concentrations with anti-HCV-positive sera from two patients infected with HCV genotype 1a or 1b or a pool of anti-HCV-negative control sera (NC; dilution, 1:50). HCV-LP-antibody complexes were added to HuH-7 cells. After the removal of nonbound HCV-LP-antibody complexes by washing the cells in PBS-2% BSA, binding of HCV-LPs was detected by flow cytometry using mouse monoclonal anti-E2 or human polyclonal anti-HCV antibodies (insets) as described in the legends to Fig. 1 and 2. (A and B) Genotype-dependent inhibition of HCV-LP binding by serum from a patient infected with HCV genotype 1b. (C and D) Genotype-independent inhibition of cellular HCV-LP binding by serum from a patient infected with genotype 1a. Fluorescence intensity (FL2-Height) and relative cell numbers (Counts) are shown on the x and y axes, respectively. The insets show the corresponding results of serum-induced inhibition of HCV-LP binding detected by human polyclonal anti-HCV antibody (HCV-LP binding in the presence of control serum [Control] = 100%).