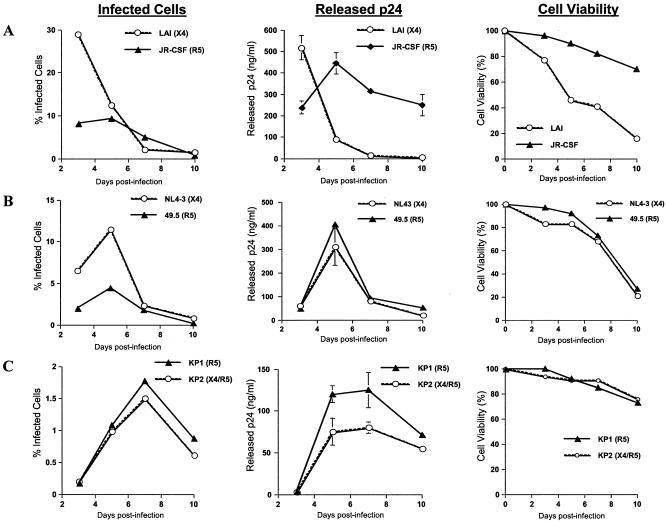
FIG. 7.
R5-infected CD4+ T cells produce more progeny virus over time than X4-infected CD4+ T cells. CD4+ T cells were isolated from PBMC and then stimulated for 72 h with CD3/CD28 antibodies prior to HIV-1 infection. At 3, 5, 7, and 10 days postinfection, the percentage of infected cells in each culture was determined by intracellular p24 staining and flow cytometry, the amount of virus released from each culture was measured by p24 ELISA, and the cell viability of each culture was determined by trypan blue exclusion assay. (A) Comparison of percentages of infected cells, viral release characteristics, and percentages of cell viability in costimulated CD4+ T-cell cultures infected with the HIV-1 molecular clones LAI (X4) and JR-CSF (R5). (B) Comparison of percentages of infected cells, viral release characteristics, and percentages of cell viability in costimulated CD4+ T-cell cultures infected with the isogenic HIV-1 strains NL4-3 (X4) and 49.5 (R5). (C) Comparison of percentages of infected cells, viral release characteristics, and percentages of cell viability in costimulated CD4+ T-cell cultures infected with the primary HIV-1 isolates KP1 (R5) and KP2 (X4/R5).