Figure 3.
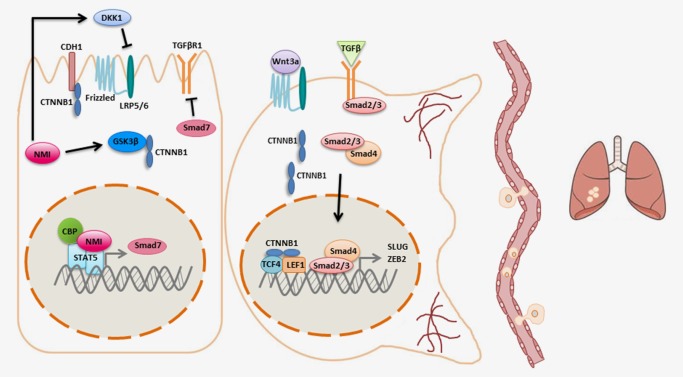
NMI inhibits cancer progression. NMI expression in epithelial cells inhibits the Wnt and TGFβ signaling pathways. NMI also increases the expression of DKK1, the secreted inhibitor of the LRP 5/6 receptor in the Wnt pathway. In addition, NMI increases levels of active GSK3β, thereby targeting β‐catenin for degradation. In parallel, NMI also binds STAT5 to enhance expression of its target gene SMAD7, the inhibitory SMAD, and subsequently dampens TGFβ signaling. In the absence of NMI, β‐catenin accumulates in the cytoplasm and is translocated to the nucleus where it binds TCF/LEF transcription factors to enhance transcription of Wnt pathway target genes. Decreased expression of NMI leads to enhanced transcription of EMT master regulators SLUG and ZEB2 downstream of TGFβ signaling. As a result, cells that have lost NMI undergo morphological changes and become more invasive and metastatic.
