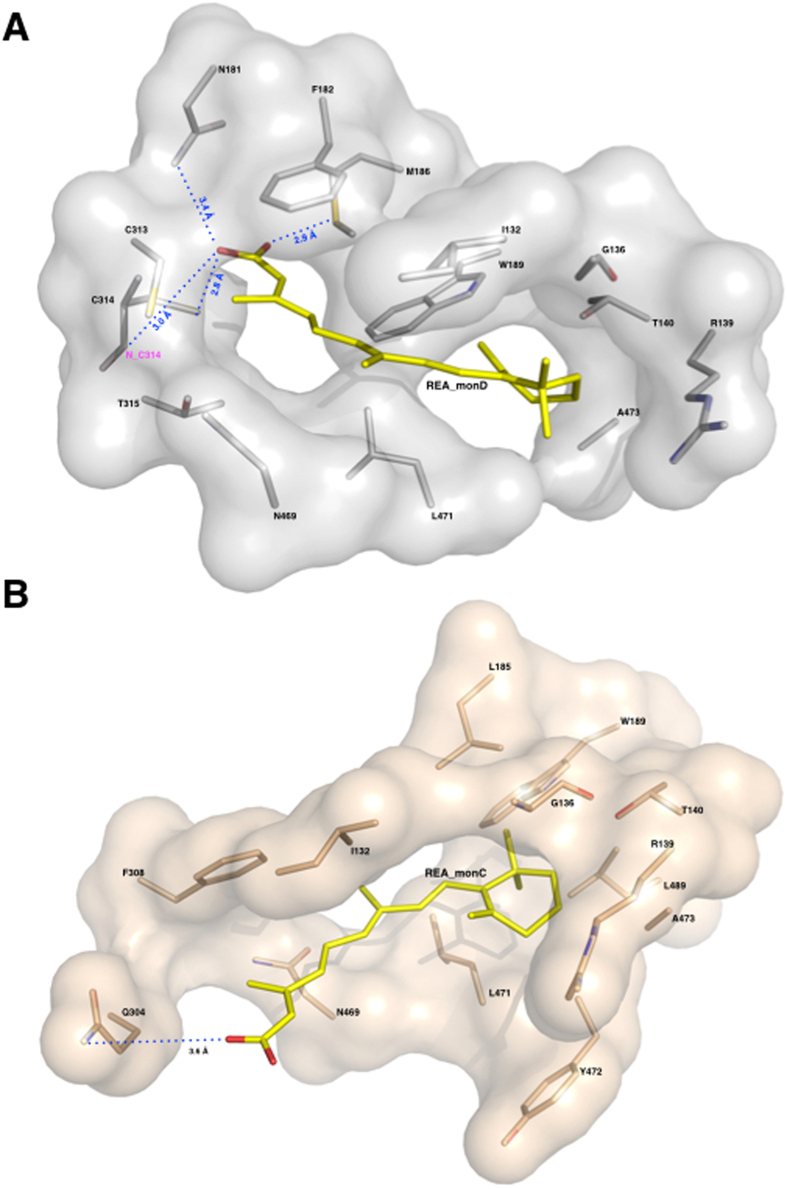
Figure 5. The REA binding site and major interactions established by REA with the protein milieu in its two conformations.
Surface representation of REA binding sites: the monomers D in grey and the monomer C in light-pink. Protein residues are represented as sticks and coloured in light-pink for monomer C and in grey for monomer D; the REA ligands (REA_C and REA_D) are shown as sticks and depicted in yellow. (A) The REA binding mode as observed in monomer D. The β-ionone ring establishes hydrophobic interactions with I132, G136, R139, T140, W189, L471 and A473. Its carboxyl group makes hydrogen bonds with C314, M186 and N181, and hydrophobic interactions with F182, C313, T315 and N469. (B) The REA binding mode as observed in monomer C. The β-ionone ring maintains the same interactions as in monomer D. On the contrary its carboxyl group significantly moves and makes hydrogen bonds with Q304 and hydrophobic interactions with F305 and N469.