Figure 6. Inhibition of erythrocyte rosettes to PvGAMA-F2 by anti-PvGAMA-Tr1 antibody and receptor specificities.
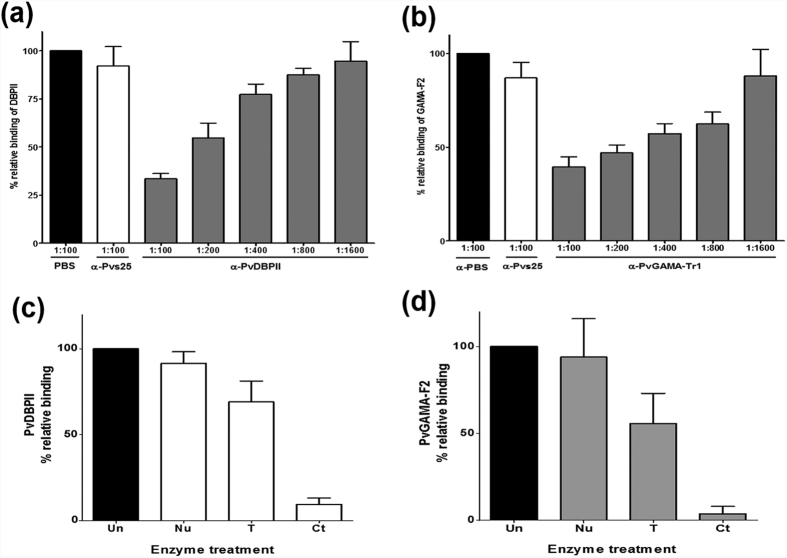
(a) HEK 293T cells were transfected with pEGFP-HSVgD1_DBPII plasmid DNA expressing a GFP-DBPII fusion protein. The cells were subsequently incubated with anti-PvDBPII rabbit sera at various dilutions before the addition of human erythrocytes. Binding was scored by counting the number of rosettes bound to HEK 293T cells in 30 microscope fields (×200 magnification). Rabbits immunized with PBS as a non-immunized control (PBS) and anti-Pvs25 (no erythrocyte-binding activity) immune rabbit sera diluted 1:100 were included as negative controls (Pvs25). (b) Inhibition of erythrocyte binding to PvGAMA-F2 expressed on HEK 293T cells by PvGAMA-Tr1 immune rabbit sera. The cells were incubated with PvGAMA-Tr1 immune rabbit sera at various dilutions before the addition of human erythrocytes. Error bars represent ± standard deviations. The erythrocyte binding abilities of HEK 293T cells transfected with pEGFP-HSVgD1_PvDBPII and PvGAMA-F2 plasmid DNA expressing a GFP-PvDBPII (c) and GFP-PvGAMA-F2 (d) were tested by incubation with untreated (Un), neuraminidase-treated (Nu), trypsin-treated (T), and chymotrypsin-treated (Ct) erythrocytes. The bars represent the standard deviation of the means of the three independent experiments.