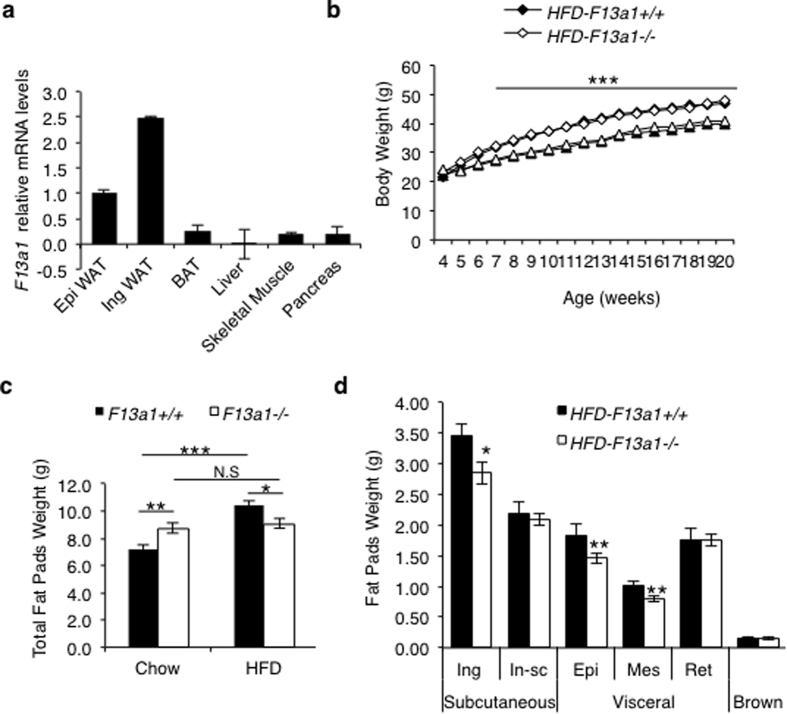
Figure 1.
F13a1−/− mice on HFD are resistant to fat accumulation (a) F13a1 mRNA expression in 1 month old mouse metabolic tissues; Epididymal (Epi WAT), Inguinal (Ing WAT); Brown adipose tissue (BAT), liver, skeletal muscle and pancreas (n = 3); Error bars represent SD (b) Body weights of F13a1−/− and F13a1+/+ mice fed chow or HFD (n = 9–11 mice/group). Significant difference between chow and HFD was observed after 4 weeks on the diets, i.e., from 8 weeks age onwards, however, no difference in weight gain between F13a1−/− and F13a1+/+ mice were observed. (c) Total fat pad weights from F13a1−/− and F13a1+/+ mice on chow or HFD show that F13a1−/− mice do not add significant fat mass (data is collected from data presented in Figure S1b,d). (d) Weights of individual fat pads of mice on HFD. Subcutaneous fat: inguinal (Ing) and inter-scapular (In-sc); visceral: epididymal (Epi), mesenteric (Mes) and retroperitoneal (Ret) fat pads (n = 10–16 mice/group). Error bars represent SEM; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; N.S.-Not Significant.