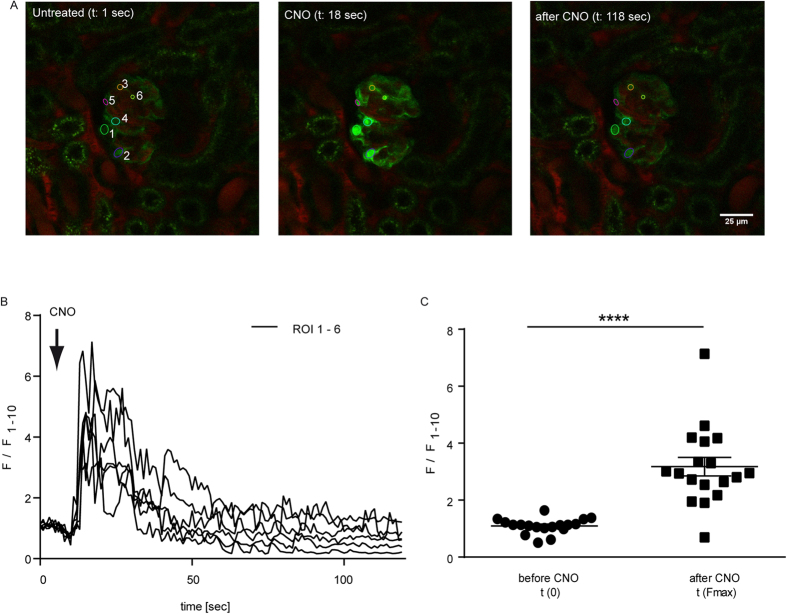
Figure 4. Administration of CNO leads to increased Ca2+-levels in podocytes in vivo.
(A) Glomeruli of ROSA26hM3D/wt; NPHS2.Cretg/wt; GCaMP3tg/wt mice were visualised in the intact kidney in vivo using a Multi-Photon-microscope. CNO (5 mg/kg) was injected i.a. after 10 sec and caused an immediate increase in intracellular Ca2+ levels (scale bar = 25 μm). (B) Fluorescence is depicted as F/F1–10, where the mean value of the first ten measurements (F1–10) prior to CNO stimulation was used for normalisation. Experiments were performed in three biological replicates. (C) Statistical analysis performed for Multi-Photon-imaging experiments revealed a significant increase of the intracellular Ca2+ after CNO stimulation. N = 18 cells were included in the statistical analysis (t-test p < 0.0001).