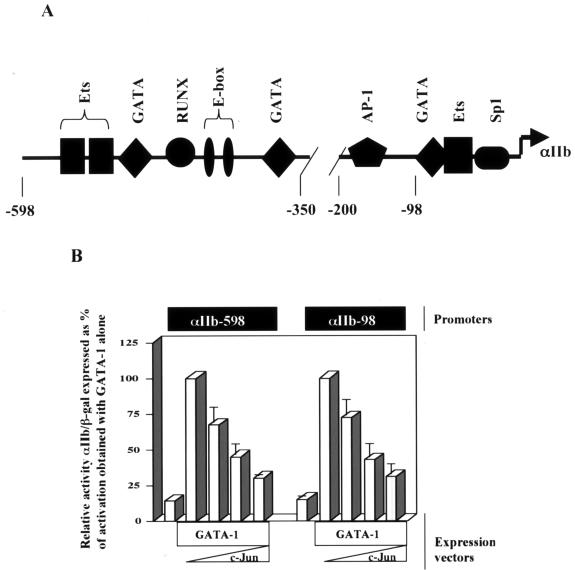
FIG. 2.
c-Jun inhibits transcriptional activation by GATA-1. (A) Map of the GATA-responsive αIIb promoter, showing positions of binding sites based on use of the TESS and TFSearch programs as previously described (14). (B) GATA-1 repression by c-Jun does not depend on cis-acting AP-1 sites. The potency of Jun-mediated repression of GATA-1 transcriptional activation was compared using two GATA-responsive reporter constructs, one possessing an AP-1 binding site (αIIb-598) and one lacking an AP-1 binding site (αIIb-98), as depicted in the diagram in A; 2 μg of the GATA-1 expression construct (pEF-GATA-1) was cotransfected with 0.2, 0.5, or 1.0 μg of the c-Jun expression construct (RSV-c-Jun). Results ± standard error of the mean of three experiments are shown as relative reporter activity compared with activation by GATA-1 alone, normalized to β-galactosidase expression.