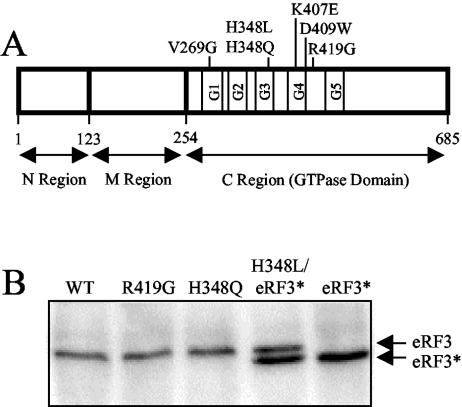
FIG. 1.
Diagram showing the location of eRF3 mutations analyzed in this study. (A) Schematic map of eRF3 showing the mutations introduced into the C-terminal GTPase domain. (B) Steady-state levels of wild-type (WT) and mutant forms of eRF3 as determined by Western blot analysis. Levels of eRF3 were measured in a sup35Δ strain (YBD498) expressing the indicated wild-type or mutant forms of eRF3 from a low-copy-number plasmid. Due to the inability of eRF3-H348L to support cell viability, it was coexpressed with a derivative of wild-type eRF3 (eRF3*) containing a small internal deletion (amino acids residues 21 to 67) in the N region. Twenty-five micrograms of total protein was loaded per lane.