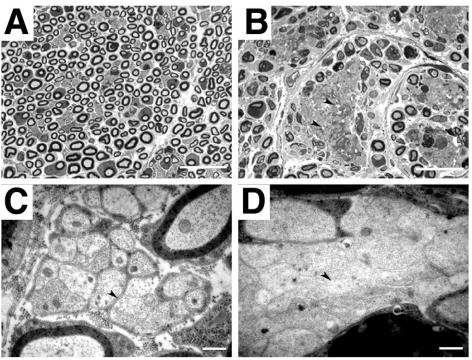
FIG. 6.
Schwann cell ablation in the sciatic nerve. (A and B) Histological analyses of semithin sections from control (A) and mutant (B) sciatic nerves, showing large areas of unmyelinated axons next to apparently normally myelinated axons (B). (C and D) Higher magnification revealed that axons were in direct contact with each other (arrowhead, D) and not separated by Schwann cell cytoplasm as in unmyelinated control axons (arrowhead, C). Very often, axons showed clear signs of degeneration, such as vacuoles and electron-dense plaques. Scale bars, 40 μm (A and B) and 2 μm (C and D).