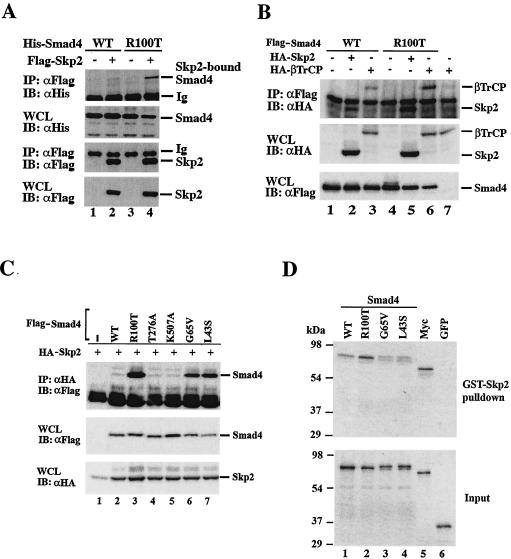
FIG. 3.
Skp2 exhibits stronger binding to cancer-derived Smad4 mutants. (A) Skp2 strongly interacts with R100T. 293T cells were transfected with Flag-tagged Skp2 and His-tagged Smad4 wild-type or R100T mutant. Immunoprecipitation-Western analysis was conducted as described for Fig. 2A. Ig, antibody heavy chain. WCL, whole-cell lysate. (B) βTRCP also binds to R100T. Transfection with Flag-Smad4 (wild type or R100T), HA-Skp2, and HA-βTRCP in 293T cells and subsequent immunoprecipitation-Western analysis were done as for panel A. (C) Skp2 strongly interacts with two other cancer-derived mutants. Immunoprecipitation-Western analysis was conducted as described for Fig. 2A except that anti-HA and anti-Flag antibodies were used for immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting, respectively. (D) Skp2 binds to Smad4 cancer mutants directly in vitro. The in vitro binding assay was done as described in Materials and Methods. WT, wild-type Smad4; Myc, positive control; GFP, negative control.