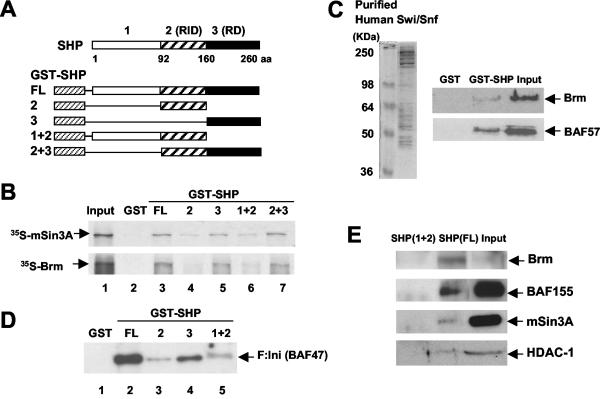
FIG. 5.
SHP interacts with mSin3A-Swi/Snf-Brm through its C-terminal repression domain in vitro. (A) Schematic diagrams of GST, full-length (FL) GST-SHP, and deletion mutants. RID and RD, receptor interacting and intrinsic repression domains, respectively; aa, amino acids. (B) 35S-labeled Brm and 35S-labeled mSin3A were synthesized in vitro, and GST pull-down assays were performed as described in Materials and Methods. Input, 20% of the total 35S-labeled proteins. (C) Swi/Snf complexes were purified using anti-Flag M2 agarose from nuclear extracts of HeLa cells stably expressing Flag-Ini 1 (F:Ini) (BAF47). GST or GST-SHP was incubated with purified Swi/Snf complex, and association of the complex with SHP was detected by Western blotting. Input, 20% of the amounts used in the binding reaction. (D and E) GST-SHP or the GST-SHP mutants were incubated with purified Swi/Snf complex (D) or HepG2 nuclear extracts (E), and association of the complex with SHP was analyzed by Western blotting using anti-Flag M2 antibody (D) or antisera against Brm, BAF155, mSin3A, and HDAC-1 (E).