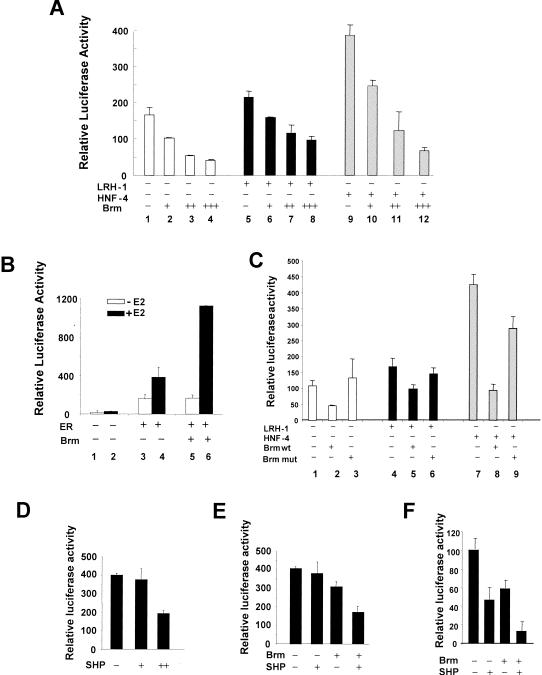
FIG. 6.
Brm represses CYP7A1 promoter activity and further enhances SHP-mediated CYP7A1 repression. (A) SW13 cells were cotransfected with (+) 100 ng of 371CYP7A1-luc and either empty vector or LRH-1 or HNF-4 expression vector, along with 0 (−), 50 (+), 200 (++), or 700 (+++) ng of pcDNA3-Brm. (B) SW13 cells were transfected with 100 ng of 4ERE-tk-luc, 20 ng of CMV-hERα (ER), and 700 ng of pcDNA3-Brm (Brm). Twenty hours after transfection, ethanol or estradiol (E2; 10 nM) was added. (C) SW13 cells were transfected with 100 ng of CYP7A1-luc and either 100 ng of empty vector or expression vectors for LRH-1 or HNF-4, along with 200 ng of pcDNA3-Brm (Brm wt) or pcDNA3-Brm ATPase mutant (Brm mut). (D) HepG2 cells were transfected with 100 ng of CYP7A1-luc and CMV β-Gal internal control plasmid, along with 0 (−), 200 (+), or 800 (++) ng of pcDNA3-human SHP. (E) HepG2 cells were transfected with 100 ng of CYP7A1-luc, along with either 200 ng of pcDNA3-SHP, 200 ng of pcDNA3-Brm, or both plasmids. (F) SW13 cells were transfected with 100 ng of CYP7A1-luc, along with 250 ng of pcDNA3-Brm, 250 ng of pcDNA3-human SHP, or both plasmids. (A to F) Cytomegalovirus β-Gal was included as an internal control, and the values plotted are the ratios of luciferase activity to β-Gal. Standard errors of the mean are indicated by the error bars (n = 3). The empty vector pcDNA3 was added as needed so that the same amount of expression vector was present in each transfection. Reproducible results were obtained from three independent transfections of triplicate assays.