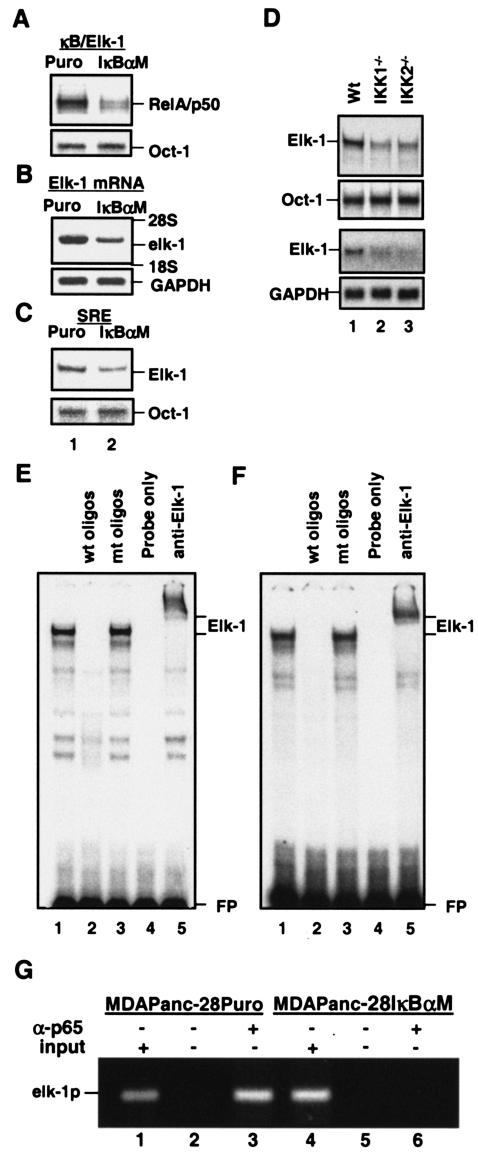
FIG. 5.
NF-κB activity regulates elk-1 expression. (A) EMSAs were performed with the nuclear extracts isolated from MDAPanc-28/Puro and MDAPanc-28/IκBαM cells to determine the NF-κB binding activity to the NF-κB motif on the elk-1 promoter with an Oct-1 probe as a control. (B) elk-1 mRNA expression was determined by Northern blot analysis with RNA from MDAPanc-28/Puro and MDAPanc-28/IκBαM cells with elk-1 cDNA and gapdh probe as a loading control. (C) Elk-1 DNA binding activity on SRE from the c-fos promoter was determined by EMSA with the nuclear extracts from MDAPanc-28/Puro and MDAPanc-28/IκBαM cells (A) and an Oct-1 probe as a control. (D) EMSAs were performed with the nuclear extracts isolatedfrom wild-type (Wt), IKK1−/−, and IKK2−/− MEF cells to determine the Elk-1 DNA binding activity with the SRE probe. An Oct-1 probe was used as a control for loading. The expression of elk-1 was determined by Northern blot analysis with the RNA isolated from wild-type, IKK1−/−, and IKK2−/− MEF cells with mouse elk-1 cDNA and gapdh probes. (E and F) Elk-1 activity in MDAPanc-28/Puro (E) and wild-type MEF (F) cells was determined by competition and supershift assay with 10 μg of nuclear extract with a 50× excess of unlabeled wild-type and mutant Elk-1 probe (lanes 2 and 3) and anti-Elk-1 antibody as indicated. FP, free probe. (G) ChIP assays were performed with MDAPanc-28/Puro and MDAPanc-28/IκBαM cells with and without anti-p65 (NF-κB) antibody as indicated.